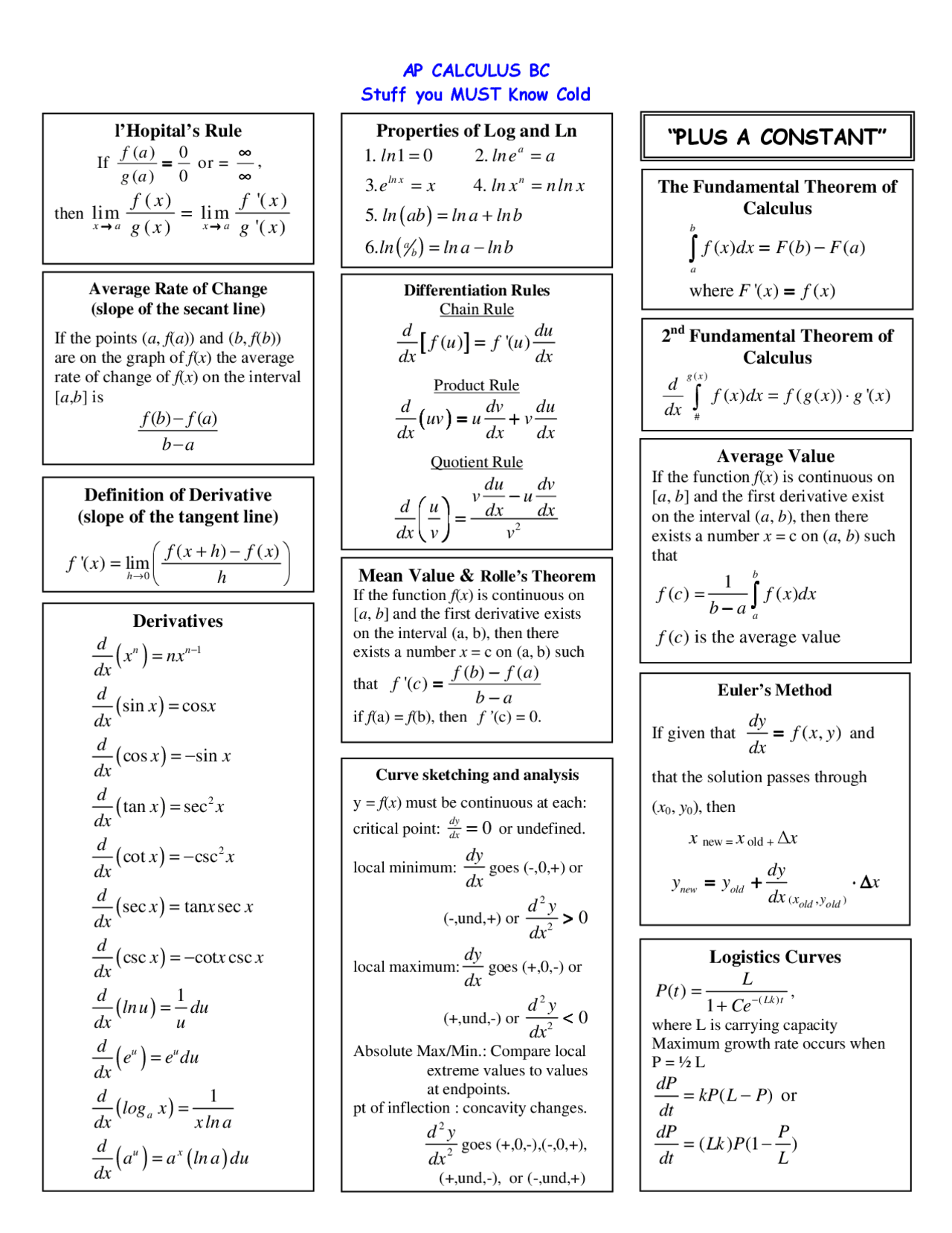
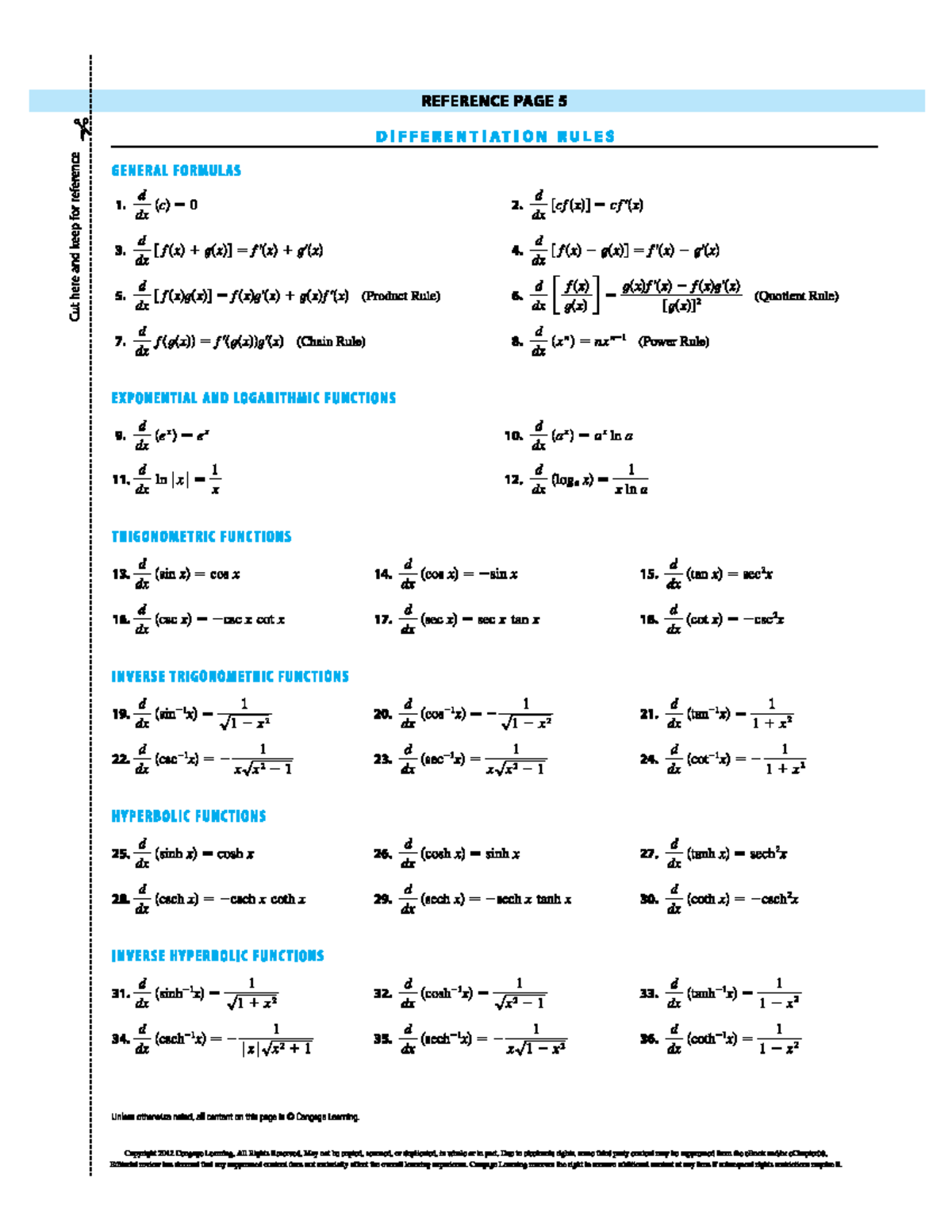
Calculus Equation Sheet
Calculus Equation Sheet - Find all (x,y) points such that rf. X c is an absolute minimum of f x if f ( c ) £ f ( x ) for all x in the domain. Web x!1 except we require x large and negative. X = c is an absolute maximum of f ( x ) if f ( c ) 3 f ( x ) for all x in the domain. Use second derivative test for whether points are local max, min, or saddle second partial derivative test 1. Extrema relative (local) extrema x = c is a relative (or local). Web solve system of equations for x and y 3. Plug back into original equation for z. We say lim f(x) = 1 if we can x!a make f(x) arbitrarily large (and positive) by taking x sufficiently close to a (on either side of a) without letting x = a. Web l'hospita1' if lim lim s rule o or lim then, = lim a is a number, or lim f (x) = lim f (x) (þt lim f (x) does not exist inflection points x=c is a inflection point of f (x) if the
Find all (x,y) points such that rf. X c is an absolute minimum of f x if f ( c ) £ f ( x ) for all x in the domain. Extrema relative (local) extrema x = c is a relative (or local). X = c is an absolute maximum of f ( x ) if f ( c ) 3 f ( x ) for all x in the domain. We say lim f(x) = 1 if we can x!a make f(x) arbitrarily large (and positive) by taking x sufficiently close to a (on either side of a) without letting x = a. Plug back into original equation for z. Web l'hospita1' if lim lim s rule o or lim then, = lim a is a number, or lim f (x) = lim f (x) (þt lim f (x) does not exist inflection points x=c is a inflection point of f (x) if the Web solve system of equations for x and y 3. Web x!1 except we require x large and negative. Use second derivative test for whether points are local max, min, or saddle second partial derivative test 1.
X = c is an absolute maximum of f ( x ) if f ( c ) 3 f ( x ) for all x in the domain. Web x!1 except we require x large and negative. Use second derivative test for whether points are local max, min, or saddle second partial derivative test 1. We say lim f(x) = 1 if we can x!a make f(x) arbitrarily large (and positive) by taking x sufficiently close to a (on either side of a) without letting x = a. Extrema relative (local) extrema x = c is a relative (or local). Web solve system of equations for x and y 3. Plug back into original equation for z. X c is an absolute minimum of f x if f ( c ) £ f ( x ) for all x in the domain. Find all (x,y) points such that rf. Web l'hospita1' if lim lim s rule o or lim then, = lim a is a number, or lim f (x) = lim f (x) (þt lim f (x) does not exist inflection points x=c is a inflection point of f (x) if the
Physics with Calculus useful equations, pt 2. From my "cheat sheet
We say lim f(x) = 1 if we can x!a make f(x) arbitrarily large (and positive) by taking x sufficiently close to a (on either side of a) without letting x = a. Web l'hospita1' if lim lim s rule o or lim then, = lim a is a number, or lim f (x) = lim f (x) (þt lim.
Vector Calc 4 Calculus, Math cheat sheet, Math formulas
Extrema relative (local) extrema x = c is a relative (or local). Web x!1 except we require x large and negative. X c is an absolute minimum of f x if f ( c ) £ f ( x ) for all x in the domain. Plug back into original equation for z. X = c is an absolute maximum.
Ap calculus bc cheat sheet Docsity
Web x!1 except we require x large and negative. Web l'hospita1' if lim lim s rule o or lim then, = lim a is a number, or lim f (x) = lim f (x) (þt lim f (x) does not exist inflection points x=c is a inflection point of f (x) if the Find all (x,y) points such that rf..
Calculus, Studying math, Learning mathematics
Extrema relative (local) extrema x = c is a relative (or local). Web l'hospita1' if lim lim s rule o or lim then, = lim a is a number, or lim f (x) = lim f (x) (þt lim f (x) does not exist inflection points x=c is a inflection point of f (x) if the Use second derivative test.
Ap Calculus Bc Formula Sheet College Board Goimages Go
Find all (x,y) points such that rf. Use second derivative test for whether points are local max, min, or saddle second partial derivative test 1. X = c is an absolute maximum of f ( x ) if f ( c ) 3 f ( x ) for all x in the domain. Plug back into original equation for z..
has some problems and solutions that might help studying. Calculus
We say lim f(x) = 1 if we can x!a make f(x) arbitrarily large (and positive) by taking x sufficiently close to a (on either side of a) without letting x = a. X c is an absolute minimum of f x if f ( c ) £ f ( x ) for all x in the domain. Web solve.
Mr. Suominen's Math Homepage AP Calculus
Find all (x,y) points such that rf. Web solve system of equations for x and y 3. We say lim f(x) = 1 if we can x!a make f(x) arbitrarily large (and positive) by taking x sufficiently close to a (on either side of a) without letting x = a. X c is an absolute minimum of f x if.
Calculus Equations Sheet
Web solve system of equations for x and y 3. X = c is an absolute maximum of f ( x ) if f ( c ) 3 f ( x ) for all x in the domain. X c is an absolute minimum of f x if f ( c ) £ f ( x ) for all x.
Calculus2 Formulaesheet MAST10006 Calculus 2 ix ∫ Formulae Sheet sinx
Find all (x,y) points such that rf. Use second derivative test for whether points are local max, min, or saddle second partial derivative test 1. Plug back into original equation for z. X c is an absolute minimum of f x if f ( c ) £ f ( x ) for all x in the domain. Web l'hospita1' if.
has some problems and solutions that might help studying. Calculus
We say lim f(x) = 1 if we can x!a make f(x) arbitrarily large (and positive) by taking x sufficiently close to a (on either side of a) without letting x = a. Web x!1 except we require x large and negative. X c is an absolute minimum of f x if f ( c ) £ f ( x.
Web X!1 Except We Require X Large And Negative.
Web solve system of equations for x and y 3. Web l'hospita1' if lim lim s rule o or lim then, = lim a is a number, or lim f (x) = lim f (x) (þt lim f (x) does not exist inflection points x=c is a inflection point of f (x) if the X = c is an absolute maximum of f ( x ) if f ( c ) 3 f ( x ) for all x in the domain. Plug back into original equation for z.
X C Is An Absolute Minimum Of F X If F ( C ) £ F ( X ) For All X In The Domain.
We say lim f(x) = 1 if we can x!a make f(x) arbitrarily large (and positive) by taking x sufficiently close to a (on either side of a) without letting x = a. Use second derivative test for whether points are local max, min, or saddle second partial derivative test 1. Find all (x,y) points such that rf. Extrema relative (local) extrema x = c is a relative (or local).