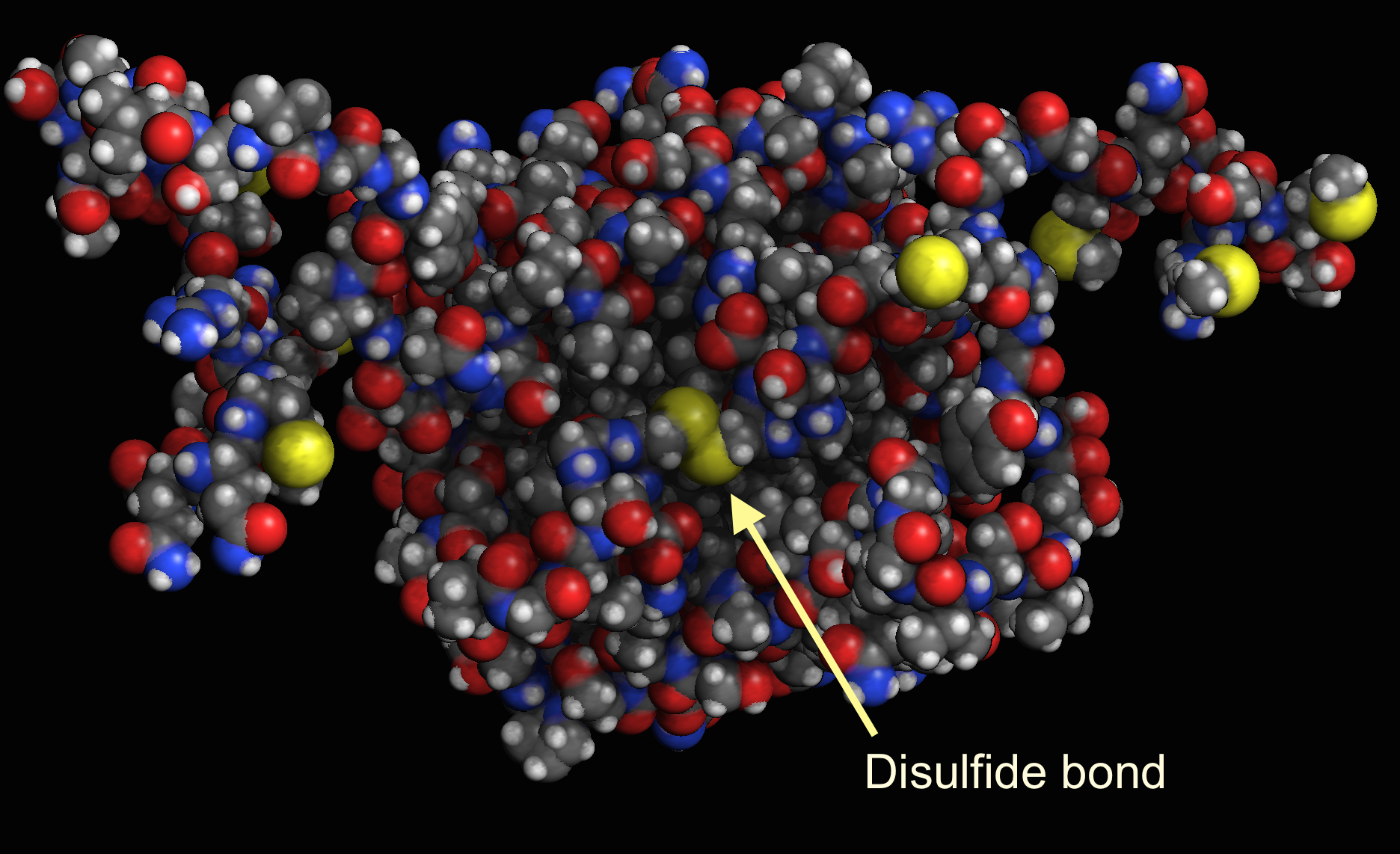
Can Methionine Form Disulfide Bonds
Can Methionine Form Disulfide Bonds - Web is cysteine the only amino acid that can form disulfide bonds? Disulfide bonds in proteins are formed between the thiol groups of cysteine residues by the process of oxidative folding. Web methionine residues as endogenous antioxidants in proteins. Web what can form disulfide bonds? An s− anion from one sulfhydryl group acts as a nucleophile, attacking the side chain of a second cysteine to create a disulfide bond, and in the process releases electrons (reducing equivalents) for transfer. Web cystine is composed of two cysteines linked by a disulfide bond (shown here in its neutral form). Cysteine residues disulfide bonds in proteins are formed between the thiol groups of cysteine residues by the process of oxidative folding. Web the cysteine amino acid group is the only amino acid capable of forming disulfide bonds, and thus can only do so with other cysteine groups. Thus methionine is more hydrophobic, sterically. Web answer (1 of 4):
Web disulfide bond formation involves a reaction between the sulfhydryl (sh) side chains of two cysteine residues: Web answer (1 of 4): Disulfide bonds in proteins are formed between the thiol groups of cysteine residues by the process of oxidative folding. Cysteine residues function in the catalytic cycle of many enzymes, and they can form disulfide bonds that contribute to protein structure. An s− anion from one sulfhydryl group acts as a nucleophile, attacking the side chain of a second cysteine to create a disulfide bond, and in the process releases electrons (reducing equivalents) for transfer. Thus methionine is more hydrophobic, sterically. Web the cysteine amino acid group is the only amino acid capable of forming disulfide bonds, and thus can only do so with other cysteine groups. Web methionine residues as endogenous antioxidants in proteins. Cysteine residues disulfide bonds in proteins are formed between the thiol groups of cysteine residues by the process of oxidative folding. Web what can form disulfide bonds?
Web methionine residues as endogenous antioxidants in proteins. Disulfide bonds in proteins are formed between the thiol groups of cysteine residues by the process of oxidative folding. Web disulfide bond formation involves a reaction between the sulfhydryl (sh) side chains of two cysteine residues: An s− anion from one sulfhydryl group acts as a nucleophile, attacking the side chain of a second cysteine to create a disulfide bond, and in the process releases electrons (reducing equivalents) for transfer. Web is cysteine the only amino acid that can form disulfide bonds? Cysteine residues function in the catalytic cycle of many enzymes, and they can form disulfide bonds that contribute to protein structure. Cysteine residues disulfide bonds in proteins are formed between the thiol groups of cysteine residues by the process of oxidative folding. Web answer (1 of 4): Web cystine is composed of two cysteines linked by a disulfide bond (shown here in its neutral form). Web the cysteine amino acid group is the only amino acid capable of forming disulfide bonds, and thus can only do so with other cysteine groups.
Disulfide bond wikidoc
Disulfide bonds in proteins are formed between the thiol groups of cysteine residues by the process of oxidative folding. Thus methionine is more hydrophobic, sterically. Cysteine residues disulfide bonds in proteins are formed between the thiol groups of cysteine residues by the process of oxidative folding. Web methionine residues as endogenous antioxidants in proteins. Web disulfide bond formation involves a.
Arrangement of disulfide bonds in mature proteins. Download
Web answer (1 of 4): An s− anion from one sulfhydryl group acts as a nucleophile, attacking the side chain of a second cysteine to create a disulfide bond, and in the process releases electrons (reducing equivalents) for transfer. Web is cysteine the only amino acid that can form disulfide bonds? Web what can form disulfide bonds? Web the cysteine.
Mechanisms of cleavage of allosteric disulfide bonds. Disulfide bond
Cysteine residues function in the catalytic cycle of many enzymes, and they can form disulfide bonds that contribute to protein structure. Web methionine residues as endogenous antioxidants in proteins. Web disulfide bond formation involves a reaction between the sulfhydryl (sh) side chains of two cysteine residues: Web answer (1 of 4): Cysteine residues disulfide bonds in proteins are formed between.
Chapter 2 Protein Structure Chemistry
Web methionine residues as endogenous antioxidants in proteins. Cysteine residues disulfide bonds in proteins are formed between the thiol groups of cysteine residues by the process of oxidative folding. Web answer (1 of 4): Web is cysteine the only amino acid that can form disulfide bonds? An s− anion from one sulfhydryl group acts as a nucleophile, attacking the side.
Geometry of a disulfide bond. The covalent bond between the sulfur
Thus methionine is more hydrophobic, sterically. Cysteine residues function in the catalytic cycle of many enzymes, and they can form disulfide bonds that contribute to protein structure. An s− anion from one sulfhydryl group acts as a nucleophile, attacking the side chain of a second cysteine to create a disulfide bond, and in the process releases electrons (reducing equivalents) for.
Protein Secretion and the Endoplasmic Reticulum
Web disulfide bond formation involves a reaction between the sulfhydryl (sh) side chains of two cysteine residues: Web methionine residues as endogenous antioxidants in proteins. Web answer (1 of 4): Thus methionine is more hydrophobic, sterically. Disulfide bonds in proteins are formed between the thiol groups of cysteine residues by the process of oxidative folding.
Why Can'T Methionine Form Disulfide Bonds? The 8 Top Answers
Web methionine residues as endogenous antioxidants in proteins. Web cystine is composed of two cysteines linked by a disulfide bond (shown here in its neutral form). Cysteine residues function in the catalytic cycle of many enzymes, and they can form disulfide bonds that contribute to protein structure. An s− anion from one sulfhydryl group acts as a nucleophile, attacking the.
The methionine at peptide position 5 alters significantly the
Web the cysteine amino acid group is the only amino acid capable of forming disulfide bonds, and thus can only do so with other cysteine groups. An s− anion from one sulfhydryl group acts as a nucleophile, attacking the side chain of a second cysteine to create a disulfide bond, and in the process releases electrons (reducing equivalents) for transfer..
Along came a spider ScienceBlogs
Web methionine residues as endogenous antioxidants in proteins. An s− anion from one sulfhydryl group acts as a nucleophile, attacking the side chain of a second cysteine to create a disulfide bond, and in the process releases electrons (reducing equivalents) for transfer. Web cystine is composed of two cysteines linked by a disulfide bond (shown here in its neutral form)..
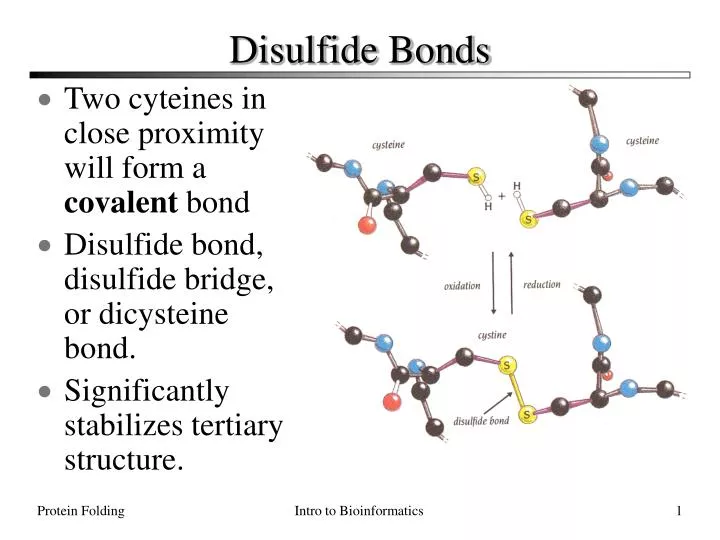
PPT Disulfide Bonds PowerPoint Presentation ID165240
Cysteine residues disulfide bonds in proteins are formed between the thiol groups of cysteine residues by the process of oxidative folding. Web answer (1 of 4): Web disulfide bond formation involves a reaction between the sulfhydryl (sh) side chains of two cysteine residues: Cysteine residues function in the catalytic cycle of many enzymes, and they can form disulfide bonds that.
Web Methionine Residues As Endogenous Antioxidants In Proteins.
Web is cysteine the only amino acid that can form disulfide bonds? Web disulfide bond formation involves a reaction between the sulfhydryl (sh) side chains of two cysteine residues: Cysteine residues disulfide bonds in proteins are formed between the thiol groups of cysteine residues by the process of oxidative folding. Web cystine is composed of two cysteines linked by a disulfide bond (shown here in its neutral form).
Web Answer (1 Of 4):
An s− anion from one sulfhydryl group acts as a nucleophile, attacking the side chain of a second cysteine to create a disulfide bond, and in the process releases electrons (reducing equivalents) for transfer. Web the cysteine amino acid group is the only amino acid capable of forming disulfide bonds, and thus can only do so with other cysteine groups. Thus methionine is more hydrophobic, sterically. Disulfide bonds in proteins are formed between the thiol groups of cysteine residues by the process of oxidative folding.
Web What Can Form Disulfide Bonds?
Cysteine residues function in the catalytic cycle of many enzymes, and they can form disulfide bonds that contribute to protein structure.