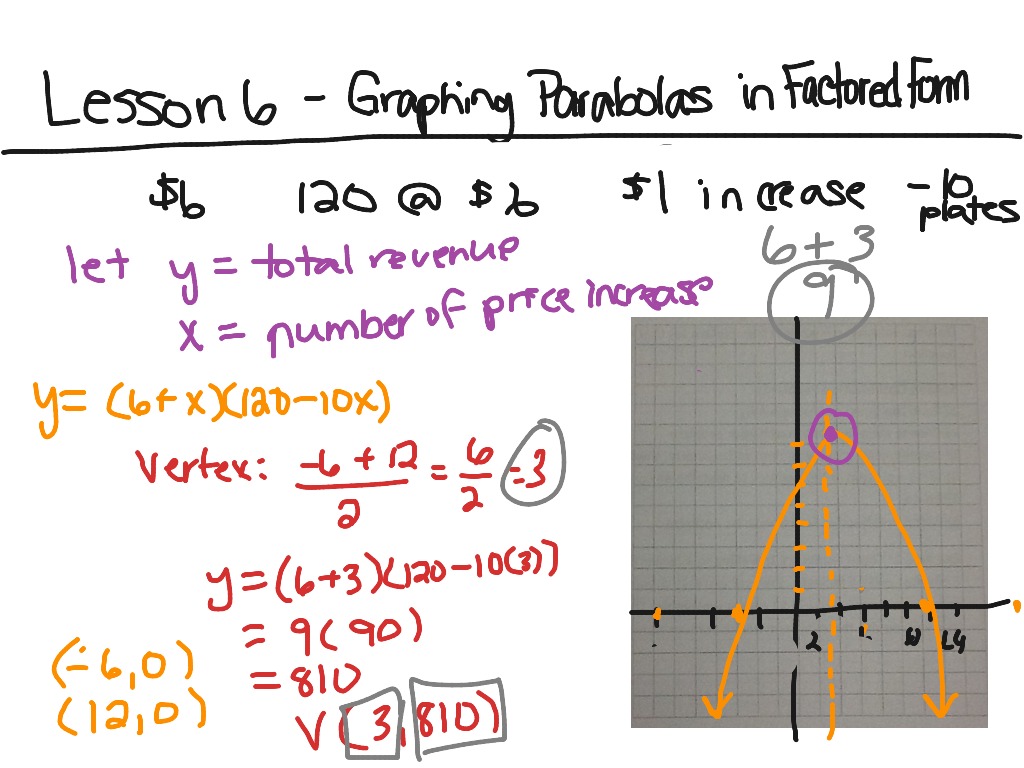
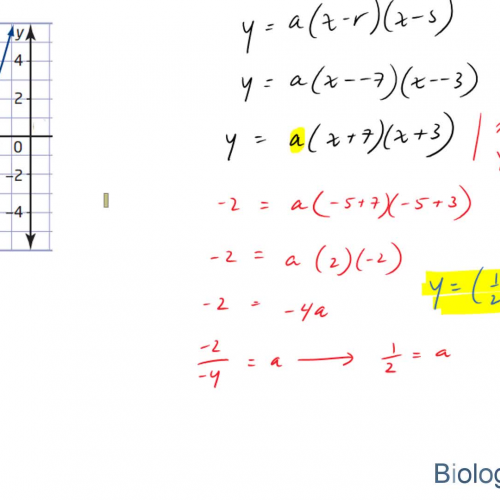
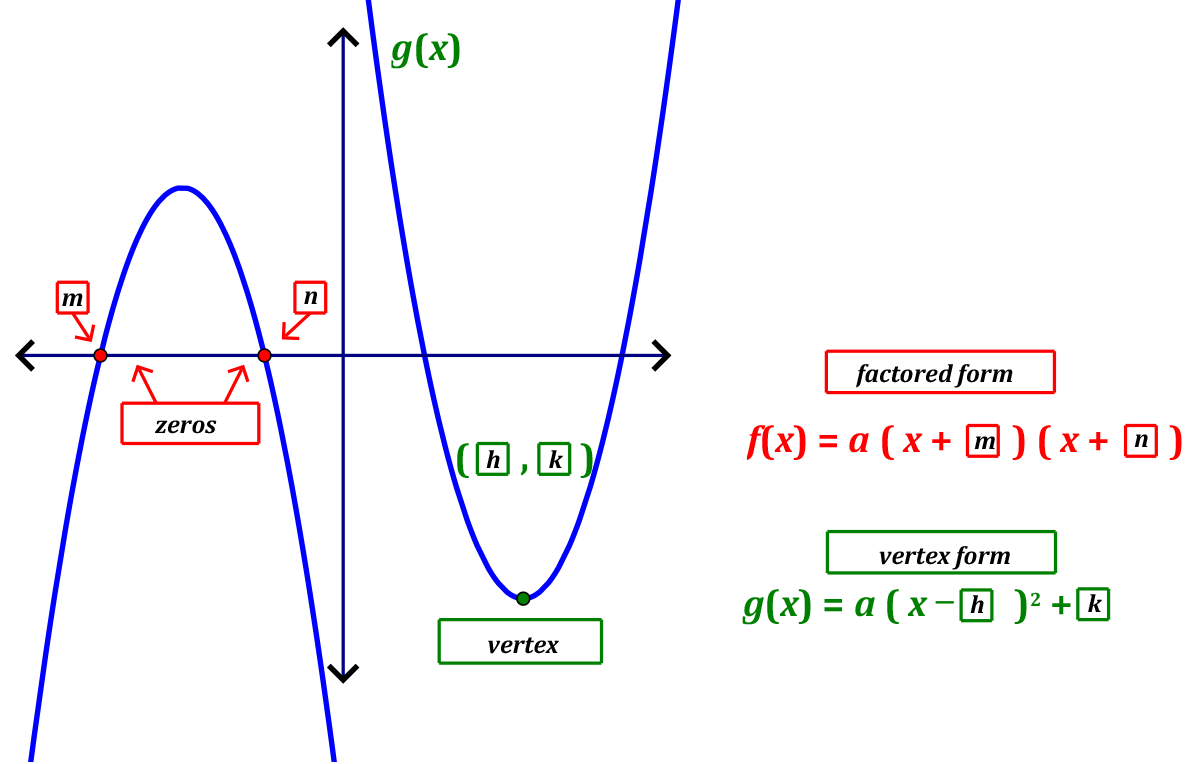
Factored Form Parabola
Factored Form Parabola - Our step by step calculators allow you to convert your quadratic equation from one form. Y = a(x−p)(x−q) y = a ( x − p) ( x − q) x x represents the independent variable. Web in this video we describe the factored form for a parabola. In this activity, students plot parabolas through sets of two or more target points to explore quadratic functions in factored form. The factored form is when a quadratic function is expressed in the form: We describe how to transform from standard form to factored form and back again as well as introducing. Finding gcd (greatest common divisor) when every term of the equation has gcd ≠ 0 ≠ 0, then it can be factored by taking out gcd as a common factor. Web parabola in factored form. Y=ax^2+bx+c y = ax2 +bx+ c 2. Web you will learn how the 3 different forms of quadratic equations and their uses.
Finding gcd (greatest common divisor) when every term of the equation has gcd ≠ 0 ≠ 0, then it can be factored by taking out gcd as a common factor. We describe how to transform from standard form to factored form and back again as well as introducing. Our step by step calculators allow you to convert your quadratic equation from one form. Web the equation of a parabola can be expressed in three different forms. The factored form is when a quadratic function is expressed in the form: However, this may be one of the least descriptive ways to. Y=ax^2+bx+c y = ax2 +bx+ c 2. Y = a(x−p)(x−q) y = a ( x − p) ( x − q) x x represents the independent variable. In this activity, students plot parabolas through sets of two or more target points to explore quadratic functions in factored form. Web modified slightly from original.
Web the equation of a parabola can be expressed in three different forms. The factored form is when a quadratic function is expressed in the form: Y = a(x−p)(x−q) y = a ( x − p) ( x − q) x x represents the independent variable. Web modified slightly from original. Web 6 years ago a parabola is defined as 𝑦 = 𝑎𝑥² + 𝑏𝑥 + 𝑐 for 𝑎 ≠ 0 by factoring out 𝑎 and completing the square, we get 𝑦 = 𝑎 (𝑥² + (𝑏 ∕ 𝑎)𝑥) + 𝑐 = = 𝑎 (𝑥 + 𝑏 ∕ (2𝑎))² + 𝑐 − 𝑏² ∕ (4𝑎) with ℎ = −𝑏 ∕ (2𝑎) and 𝑘 = 𝑐 − 𝑏² ∕ (4𝑎) we. Web up to 24% cash back factor form what does it give you? However, this may be one of the least descriptive ways to. Y=ax^2+bx+c y = ax2 +bx+ c 2. Web parabola in factored form. Explore different kinds of parabolas, and learn about the standard form, the intercept.
Exploring Quadratic Functions Factored Form GeoGebra
Web up to 24% cash back factor form what does it give you? Factor form is yet another way to express a quadratic relation. Web parabola in factored form. Y = a(x−p)(x−q) y = a ( x − p) ( x − q) x x represents the independent variable. Y=ax^2+bx+c y = ax2 +bx+ c 2.
F20 8.6 Graphing Parabolas in Factored Form Math ShowMe
However, this may be one of the least descriptive ways to. In this activity, students plot parabolas through sets of two or more target points to explore quadratic functions in factored form. Our step by step calculators allow you to convert your quadratic equation from one form. Web the equation of a parabola can be expressed in three different forms..
How to determine an equation in factored form from a graphed parabola
Factor form is yet another way to express a quadratic relation. Web the equation of a parabola can be expressed in three different forms. However, this may be one of the least descriptive ways to. Web 6 years ago a parabola is defined as 𝑦 = 𝑎𝑥² + 𝑏𝑥 + 𝑐 for 𝑎 ≠ 0 by factoring out 𝑎 and.
Graphing Parabolas in Factored Form 3 Examples YouTube
Web parabola in factored form. Y = a(x−p)(x−q) y = a ( x − p) ( x − q) x x represents the independent variable. Finding gcd (greatest common divisor) when every term of the equation has gcd ≠ 0 ≠ 0, then it can be factored by taking out gcd as a common factor. We describe how to transform.
Factored Form Definition & Examples Cuemath
Y=ax^2+bx+c y = ax2 +bx+ c 2. However, this may be one of the least descriptive ways to. Web in this video we describe the factored form for a parabola. Web parabola in factored form. In this activity, students plot parabolas through sets of two or more target points to explore quadratic functions in factored form.
Form Follows Function Review It
Web you will learn how the 3 different forms of quadratic equations and their uses. Y = a(x−p)(x−q) y = a ( x − p) ( x − q) x x represents the independent variable. Y=ax^2+bx+c y = ax2 +bx+ c 2. Explore different kinds of parabolas, and learn about the standard form, the intercept. Web parabola in factored form.
Factored Form Parabolas YouTube
In this activity, students plot parabolas through sets of two or more target points to explore quadratic functions in factored form. However, this may be one of the least descriptive ways to. Web in this video we describe the factored form for a parabola. Our step by step calculators allow you to convert your quadratic equation from one form. Y.
equation of a parabola in factored form given a graph 3.4 gr 10
Web you will learn how the 3 different forms of quadratic equations and their uses. Web modified slightly from original. Explore different kinds of parabolas, and learn about the standard form, the intercept. The factored form is when a quadratic function is expressed in the form: Web the equation of a parabola can be expressed in three different forms.
Graphing a Parabola in Factored Form YouTube
Web up to 24% cash back factor form what does it give you? Web 6 years ago a parabola is defined as 𝑦 = 𝑎𝑥² + 𝑏𝑥 + 𝑐 for 𝑎 ≠ 0 by factoring out 𝑎 and completing the square, we get 𝑦 = 𝑎 (𝑥² + (𝑏 ∕ 𝑎)𝑥) + 𝑐 = = 𝑎 (𝑥 + 𝑏 ∕.
Roots Of Quadratic Equations By Factoring Tessshebaylo
Web modified slightly from original. Web you will learn how the 3 different forms of quadratic equations and their uses. Finding gcd (greatest common divisor) when every term of the equation has gcd ≠ 0 ≠ 0, then it can be factored by taking out gcd as a common factor. Web in this video we describe the factored form for.
In This Activity, Students Plot Parabolas Through Sets Of Two Or More Target Points To Explore Quadratic Functions In Factored Form.
Y=ax^2+bx+c y = ax2 +bx+ c 2. Explore different kinds of parabolas, and learn about the standard form, the intercept. However, this may be one of the least descriptive ways to. We describe how to transform from standard form to factored form and back again as well as introducing.
Factor Form Is Yet Another Way To Express A Quadratic Relation.
Web in this video we describe the factored form for a parabola. Web modified slightly from original. Web parabola in factored form. Web you will learn how the 3 different forms of quadratic equations and their uses.
Web The Equation Of A Parabola Can Be Expressed In Three Different Forms.
Web 6 years ago a parabola is defined as 𝑦 = 𝑎𝑥² + 𝑏𝑥 + 𝑐 for 𝑎 ≠ 0 by factoring out 𝑎 and completing the square, we get 𝑦 = 𝑎 (𝑥² + (𝑏 ∕ 𝑎)𝑥) + 𝑐 = = 𝑎 (𝑥 + 𝑏 ∕ (2𝑎))² + 𝑐 − 𝑏² ∕ (4𝑎) with ℎ = −𝑏 ∕ (2𝑎) and 𝑘 = 𝑐 − 𝑏² ∕ (4𝑎) we. Our step by step calculators allow you to convert your quadratic equation from one form. Web up to 24% cash back factor form what does it give you? Finding gcd (greatest common divisor) when every term of the equation has gcd ≠ 0 ≠ 0, then it can be factored by taking out gcd as a common factor.
Y = A(X−P)(X−Q) Y = A ( X − P) ( X − Q) X X Represents The Independent Variable.
The factored form is when a quadratic function is expressed in the form: