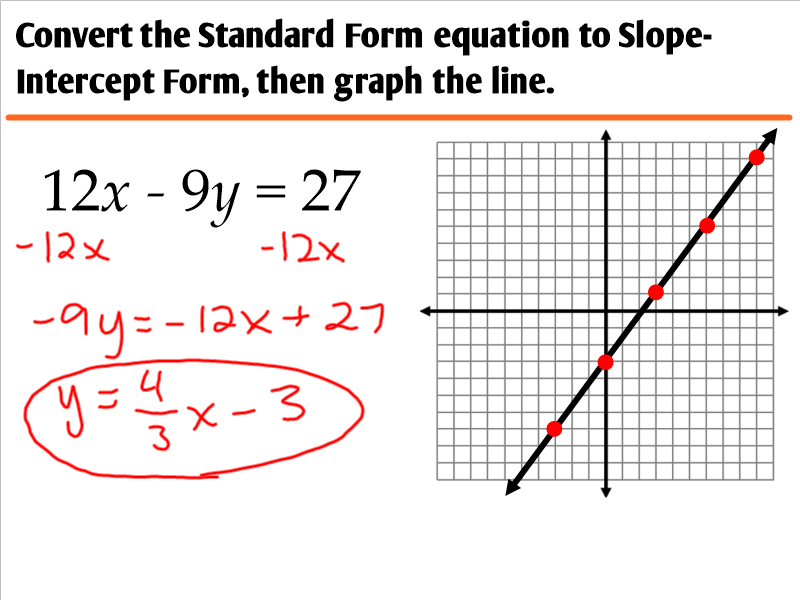
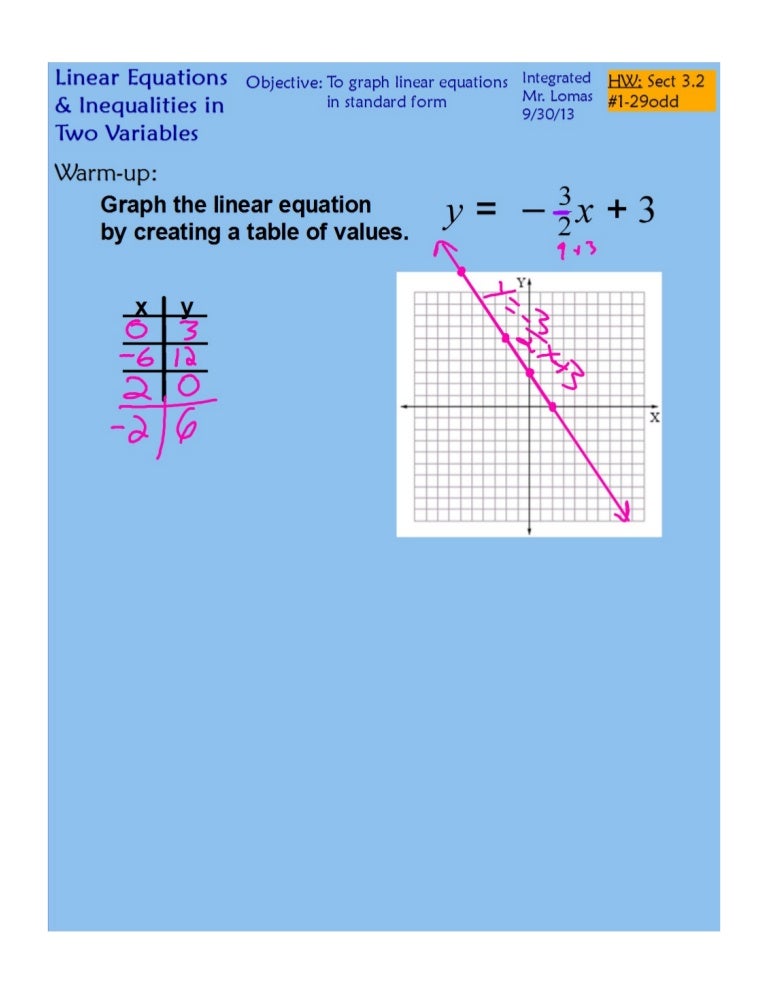
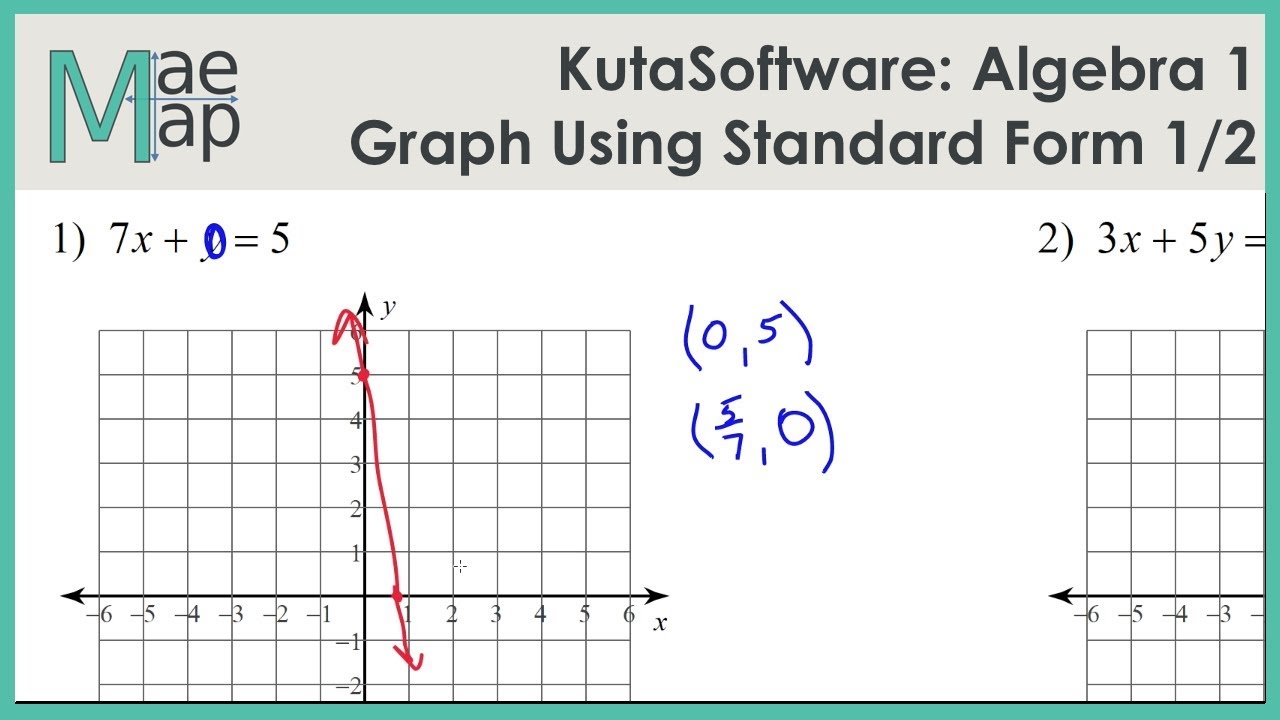
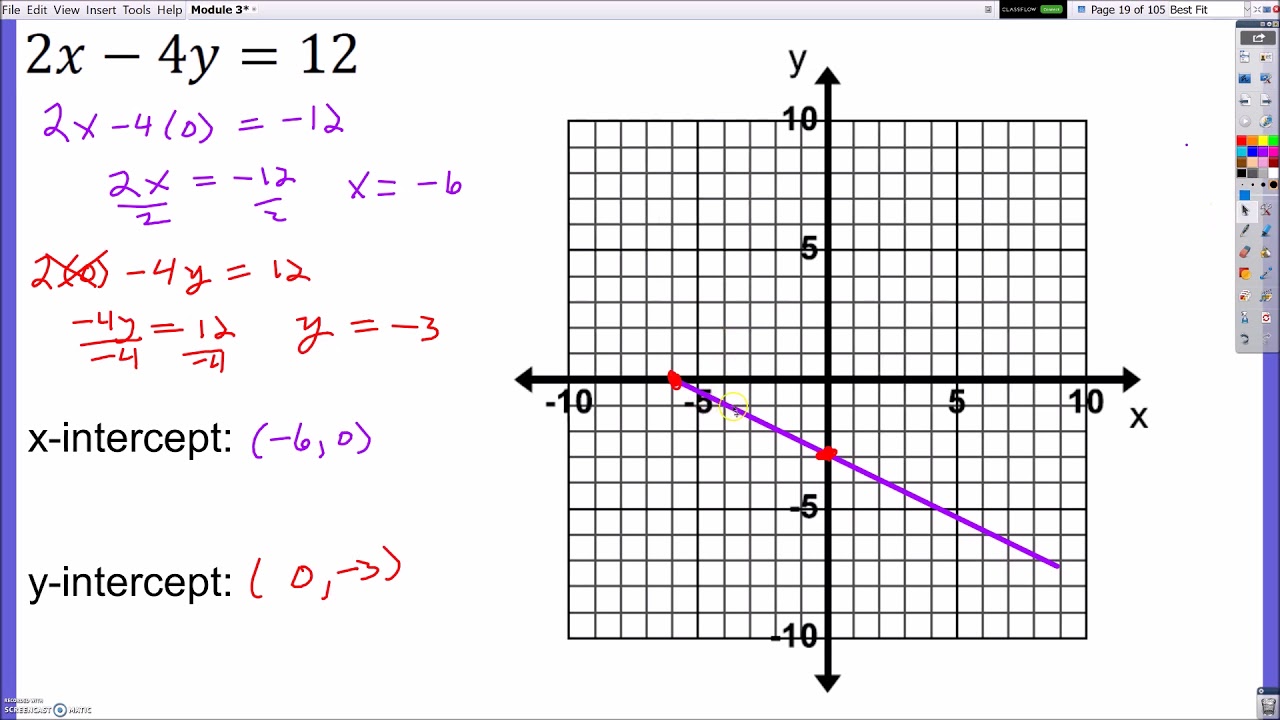
Graphing Lines Standard Form
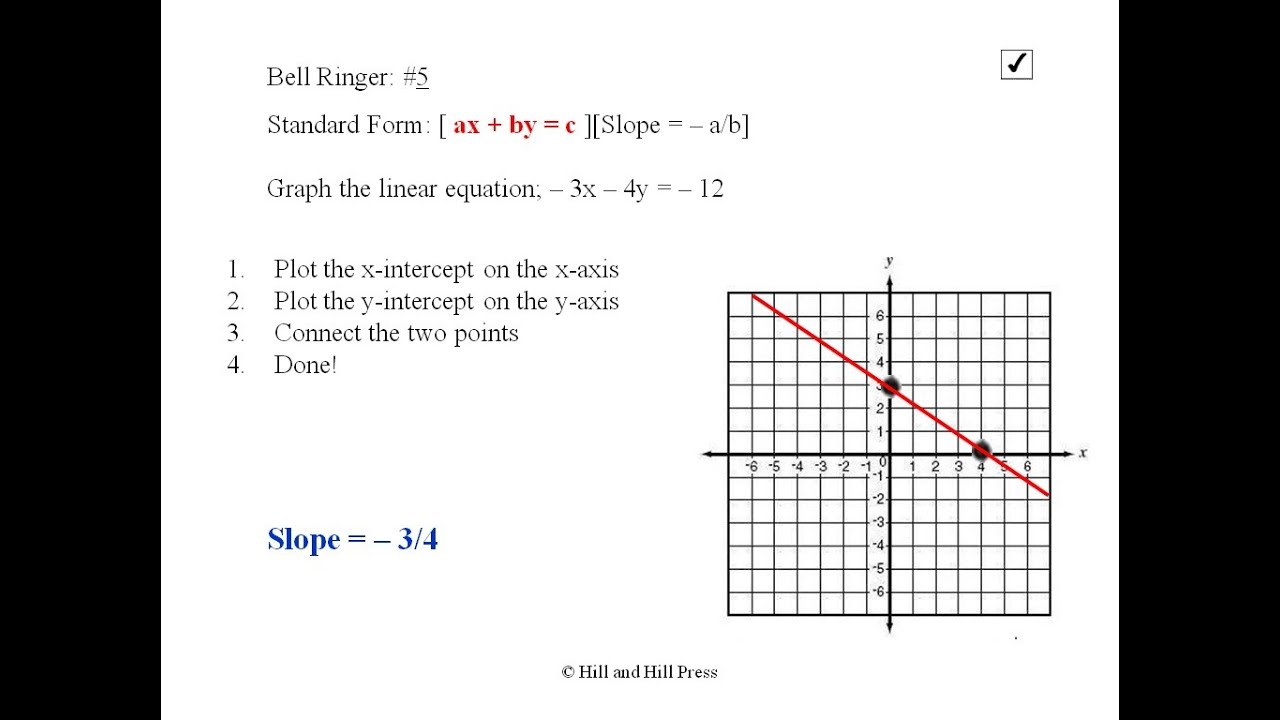
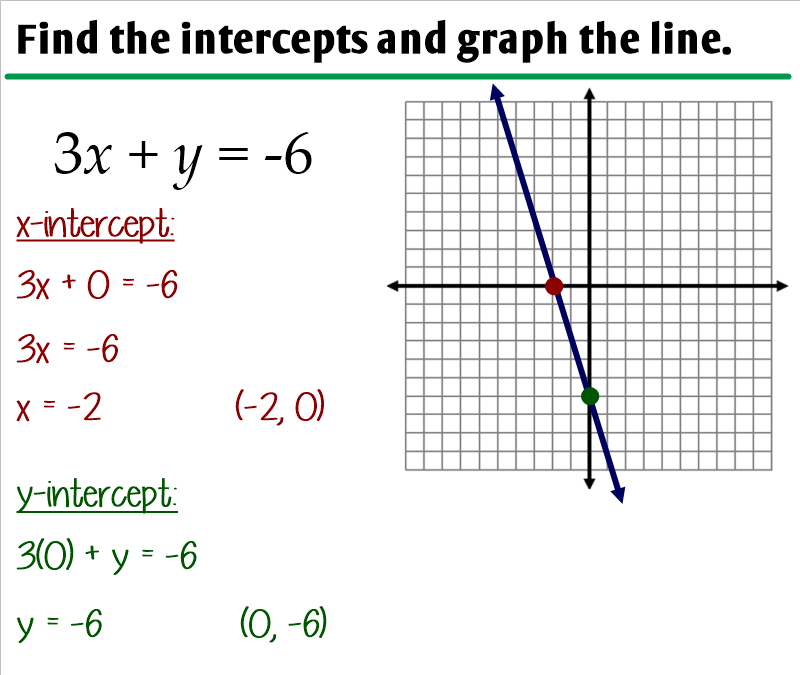
Graphing Lines Standard Form - Web instructor zach pino. • an x‑intercept is the point where a graph crosses the x‑axis. For example, 2x+3y=5 is a linear equation in standard form. Also, know how to graph the standard form and the slope. 8.ee.c.7, 8.f.a.1, hsf.if.c.7, hsf.if.c.7a google classroom you might need: Find the x‑intercept by plugging in 0 for y, then solve. ★i typically use this set of notes directly. Let's g raph 5 x − 2 y = − 15. • a y‑intercept is the point where a graph crosses the y‑axis. Ax + by = c.
Also, know how to graph the standard form and the slope. Web when a line is in standard form, there are two different ways to graph it. • a y‑intercept is the point where a graph crosses the y‑axis. Web instructor zach pino. 8.ee.c.7, 8.f.a.1, hsf.if.c.7, hsf.if.c.7a google classroom you might need: Ax + by = c. For example, 2x+3y=5 is a linear equation in standard form. When an equation is given in this form, it's pretty easy to find both intercepts (x and y). This form is also very useful when solving systems of two linear equations. Algebra 1 > unit 5 graph from linear standard form ccss.math:
When given a linear function in standard form: Web graph from linear standard form | algebra (practice) | khan academy course: This form is also very useful when solving systems of two linear equations. The second approach is to use standard form to find the x and y − intercepts of the line and connect the two. There are actually two different techniques that you can use for graphing linear equations that are written in standard form. • an x‑intercept is the point where a graph crosses the x‑axis. Web ©0 y210 r192w fk wuvtqaf dsvoafot5w halr oes sl nllc 1.d v 4asl4la orii mgwhrt6s d rjeps9eer uvhekde. Ax + by = c. Web when a line is in standard form, there are two different ways to graph it. ★i typically use this set of notes directly.
2.4 Graphing Linear Equations in Standard Form Ms. Zeilstra's Math
Let's g raph 5 x − 2 y = − 15. Also, know how to graph the standard form and the slope. When given a linear function in standard form: Ax + by = c. Web graph from linear standard form | algebra (practice) | khan academy course:
Graphing Lines Standard Form.pdf
The second approach is to use standard form to find the x and y − intercepts of the line and connect the two. There are actually two different techniques that you can use for graphing linear equations that are written in standard form. Web graph from linear standard form | algebra (practice) | khan academy course: Web the standard form.
Graphing Lines in Standard Form YouTube
Web graph from linear standard form | algebra (practice) | khan academy course: Ax + by = c. For example, 2x+3y=5 is a linear equation in standard form. Also, know how to graph the standard form and the slope. Find the x‑intercept by plugging in 0 for y, then solve.
Kuta Software Infinite Algebra 1 Graphing Lines Answers Most Freeware
Find the x‑intercept by plugging in 0 for y, then solve. Web when a line is in standard form, there are two different ways to graph it. For example, 2x+3y=5 is a linear equation in standard form. • a y‑intercept is the point where a graph crosses the y‑axis. ★i typically use this set of notes directly.
Graphing with Standard Form YouTube
8.ee.c.7, 8.f.a.1, hsf.if.c.7, hsf.if.c.7a google classroom you might need: Web instructor zach pino. This form is also very useful when solving systems of two linear equations. Let's g raph 5 x − 2 y = − 15. Ax + by = c.
Graphing Linear equations in Standard Form YouTube
Web ©0 y210 r192w fk wuvtqaf dsvoafot5w halr oes sl nllc 1.d v 4asl4la orii mgwhrt6s d rjeps9eer uvhekde. This form is also very useful when solving systems of two linear equations. • a y‑intercept is the point where a graph crosses the y‑axis. Algebra 1 > unit 5 graph from linear standard form ccss.math: 8.ee.c.7, 8.f.a.1, hsf.if.c.7, hsf.if.c.7a google.
Raspaw Graphing Lines In Standard Form Kuta
Let's g raph 5 x − 2 y = − 15. Web graph from linear standard form | algebra (practice) | khan academy course: Algebra 1 > unit 5 graph from linear standard form ccss.math: Web the standard form for linear equations in two variables is ax+by=c. Find the x‑intercept by plugging in 0 for y, then solve.
Graphing Lines in Standard Form Algebra 1 YouTube
When given a linear function in standard form: Web the standard form for linear equations in two variables is ax+by=c. Let's g raph 5 x − 2 y = − 15. Ax + by = c. When an equation is given in this form, it's pretty easy to find both intercepts (x and y).
3.4 Graphing Linear Equations in Standard Form Ms. Zeilstra's Math
When an equation is given in this form, it's pretty easy to find both intercepts (x and y). Ax + by = c. There are actually two different techniques that you can use for graphing linear equations that are written in standard form. Let's g raph 5 x − 2 y = − 15. 8.ee.c.7, 8.f.a.1, hsf.if.c.7, hsf.if.c.7a google classroom.
There Are Actually Two Different Techniques That You Can Use For Graphing Linear Equations That Are Written In Standard Form.
Web ©0 y210 r192w fk wuvtqaf dsvoafot5w halr oes sl nllc 1.d v 4asl4la orii mgwhrt6s d rjeps9eer uvhekde. ★i typically use this set of notes directly. Find the x‑intercept by plugging in 0 for y, then solve. For example, 2x+3y=5 is a linear equation in standard form.
Ax + By = C.
Web when a line is in standard form, there are two different ways to graph it. This form is also very useful when solving systems of two linear equations. The second approach is to use standard form to find the x and y − intercepts of the line and connect the two. • an x‑intercept is the point where a graph crosses the x‑axis.
8.Ee.c.7, 8.F.a.1, Hsf.if.c.7, Hsf.if.c.7A Google Classroom You Might Need:
Algebra 1 > unit 5 graph from linear standard form ccss.math: Also, know how to graph the standard form and the slope. When given a linear function in standard form: When an equation is given in this form, it's pretty easy to find both intercepts (x and y).
Web Instructor Zach Pino.
Web the standard form for linear equations in two variables is ax+by=c. Web graph from linear standard form | algebra (practice) | khan academy course: Let's g raph 5 x − 2 y = − 15. • a y‑intercept is the point where a graph crosses the y‑axis.