Line Vector Form
Line Vector Form - [3] horizontal and vertical lines Web equation of a line: Multiplying a vector by a scalar. R → = a → + λ b →, where λ is scalar. Web line defined by an equation in the case of a line in the plane given by the equation ax + by + c = 0, where a, b and c are real constants with a and b not both zero, the distance from the line to a point (x0, y0) is [1] [2] : Web unit vector form these are the unit vectors in their component form: It can be done without vectors, but vectors provide a really. It is obvious (i think) that the line is parallel to the cross product vector u × v u. Then is the direction vector for and the vector equation for is given by We'll use z as the parameter.
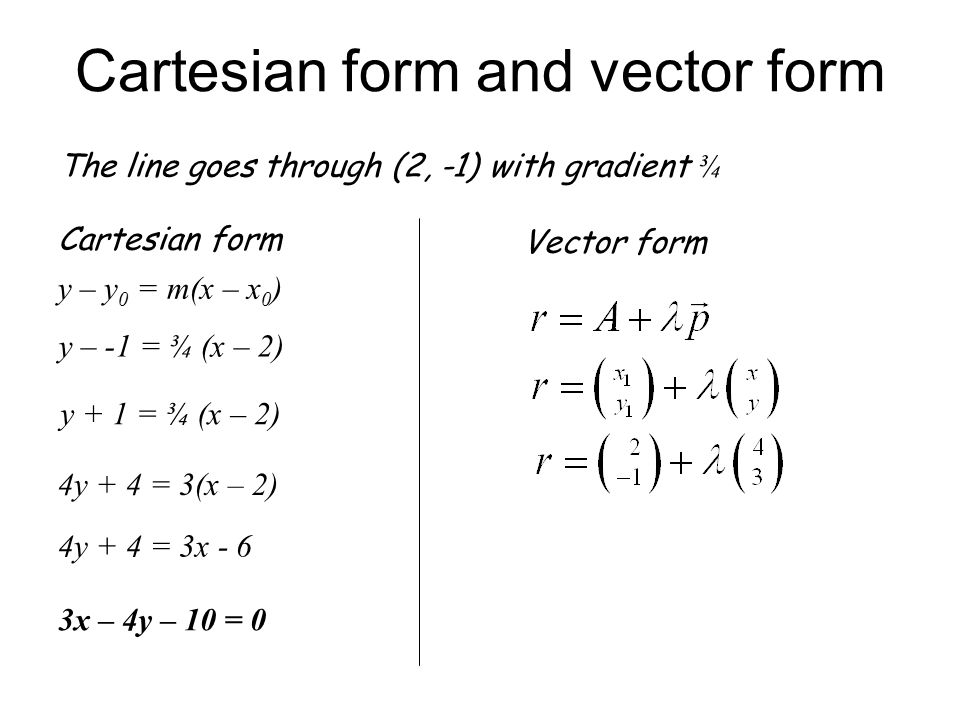
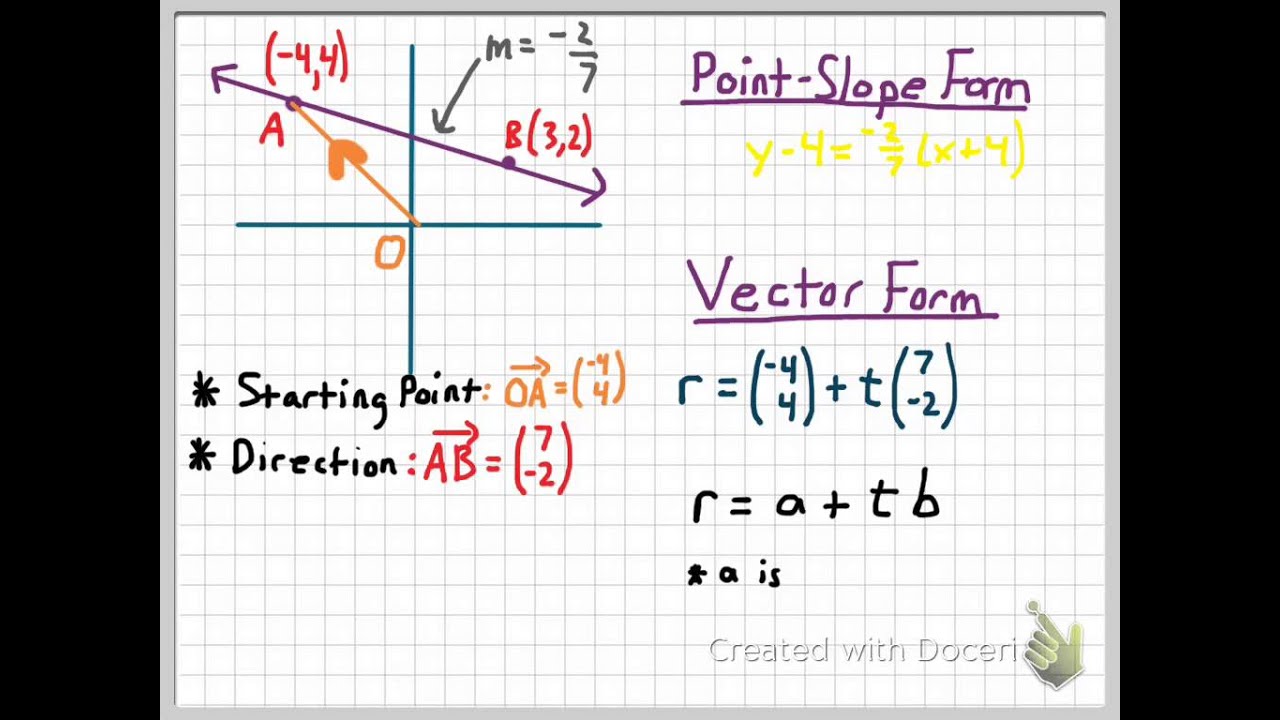
Where u = (1, 1, −1) u = ( 1, 1, − 1) and v = (2, 2, 1) v = ( 2, 2, 1) are vectors that are normal to the two planes. The vector equation of a line passing through a point and having a position vector →a a →, and parallel to a vector line →b b → is →r = →a +λ→b r → = a → + λ b →. [3] horizontal and vertical lines Web line defined by an equation in the case of a line in the plane given by the equation ax + by + c = 0, where a, b and c are real constants with a and b not both zero, the distance from the line to a point (x0, y0) is [1] [2] : The vector form of the equation of a line passing through two points with the position vector →a a →, and →b b → is →r =. This assortment of quality vectors will most likely be in line with your design needs. \lambda λ below is a parameter. It can be done without vectors, but vectors provide a really. For example, (3,4) (3,4) can be written as 3\hat i+4\hat j 3i^+4j ^. The line with gradient m and intercept c has equation.
If i have helped you then please support my work on patreon: Web the line’s vector equation is represented by its general form shown below. The position vector →r for a point between p and q is given by →r = →p + →v If (x, y, z) is on the line then z = t and x + y + t = 2 x − y + t = 0 the second equation forces y = x. Web adding vectors algebraically & graphically. For example, (3,4) (3,4) can be written as 3\hat i+4\hat j 3i^+4j ^. \hat i= (1,0) i^= (1,0) \hat j= (0,1) j ^ = (0,1) using vector addition and scalar multiplication, we can represent any vector as a combination of the unit vectors. The two given equations represent planes, and the required line is their intersection. For each $t_0$, $\vec{r}(t_0)$ is a vector starting at the origin whose endpoint is on the desired line. We will also give the symmetric equations of lines in three dimensional space.
Vector Line Png ClipArt Best
Web the vector equation of a line is an equation that is satisfied by the vector that has its head at a point of the line. Each point on the line has a different value of z. Other ways to support engineer4free <3. Web in this section we will derive the vector form and parametric form for the equation of.
Vector Form at Collection of Vector Form free for
R = r o + t v, where r o represents the initial position of the line, v is the vector indicating the direction of the line, and t is the parameter defining v ’s direction. Vector form of the equation of a line in two dimensions. For example, (3,4) (3,4) can be written as 3\hat i+4\hat j 3i^+4j ^..
General Form Equation Of A Line Tessshebaylo
The vector equation of a line passing through a point and having a position vector →a a →, and parallel to a vector line →b b → is →r = →a +λ→b r → = a → + λ b →. Want to learn more about unit vectors? The two given equations represent planes, and the required line is their.
Question Video Finding the Vector Form of the Equation of a Straight
You're already familiar with the idea of the equation of a line in two dimensions: T = x + 1 −2 t = y − 1 3 t = z − 2 t = x + 1 − 2 t = y − 1 3 t = z − 2 so you have: It can be done without vectors, but.
Line seamless pattern 557703 Vector Art at Vecteezy
Note as well that while these forms can also be useful for lines in two dimensional space. If 𝐴 ( 𝑥, 𝑦) and 𝐵 ( 𝑥, 𝑦) are distinct points on a line, then one vector form of the equation of the line through 𝐴 and 𝐵 is given by ⃑ 𝑟 = ( 𝑥, 𝑦) + 𝑡 ( 𝑥.
Vector Equation of a Line YouTube
This vector is not, in general, a vector that ''lies'' on the line, unless the line passes through the origin (that is the common starting point of all vectors). When we try to specify a line in three dimensions (or in n dimensions), however, things get more involved. Want to learn more about unit vectors? This assortment of quality vectors.
Lesson Video Equation of a Straight Line Vector Form Nagwa
This is called the symmetric equation for the line. Web the vector equation of a line is an equation that is satisfied by the vector that has its head at a point of the line. Web the vector equation of a line. The position vector →r for a point between p and q is given by →r = →p +.
Vector Equation Line & Plane Equations, Formula, Examples
Web x − x 0 d x = y − y 0 d y. The two given equations represent planes, and the required line is their intersection. ⎡⎣⎢x y z⎤⎦⎥ =⎡⎣⎢−1 1 2 ⎤⎦⎥ + t⎡⎣⎢−2 3 1 ⎤⎦⎥ [ x y z] = [ − 1 1 2] + t [ − 2 3 1] for the symmetric form.
5. Example of Vector Form of a Line YouTube
Vector form of the equation of a line in two dimensions. Web x − x 0 d x = y − y 0 d y. No need to get in line to start using them! The line with gradient m and intercept c has equation. It can be done without vectors, but vectors provide a really.
The Vector Equation Of A Straight Line Passing Through A Fixed Point With Position Vector A → And Parallel To A Given Vector B → Is.
Magnitude & direction to component. The vector form of the equation of a line passing through two points with the position vector →a a →, and →b b → is →r =. We'll use z as the parameter. [3] horizontal and vertical lines
Web The Two Methods Of Forming A Vector Form Of The Equation Of A Line Are As Follows.
We will also give the symmetric equations of lines in three dimensional space. P.14 the point on this line which is closest to (x0, y0) has coordinates: Web write the equation of the line in general form, vector form, or parametric form. T = x + 1 −2 t = y − 1 3 t = z − 2 t = x + 1 − 2 t = y − 1 3 t = z − 2 so you have:
If I Have Helped You Then Please Support My Work On Patreon:
This is called the symmetric equation for the line. If 𝐴 ( 𝑥, 𝑦) and 𝐵 ( 𝑥, 𝑦) are distinct points on a line, then one vector form of the equation of the line through 𝐴 and 𝐵 is given by ⃑ 𝑟 = ( 𝑥, 𝑦) + 𝑡 ( 𝑥 − 𝑥, 𝑦 − 𝑦). Note as well that while these forms can also be useful for lines in two dimensional space. No need to get in line to start using them!
They're Scalable, Modifiable, Adaptable And, Most Importantly, Downloadable.
Let and be the position vectors of these two points, respectively. Web the line’s vector equation is represented by its general form shown below. \hat i= (1,0) i^= (1,0) \hat j= (0,1) j ^ = (0,1) using vector addition and scalar multiplication, we can represent any vector as a combination of the unit vectors. The vector equation of a line passing through a point and having a position vector →a a →, and parallel to a vector line →b b → is →r = →a +λ→b r → = a → + λ b →.