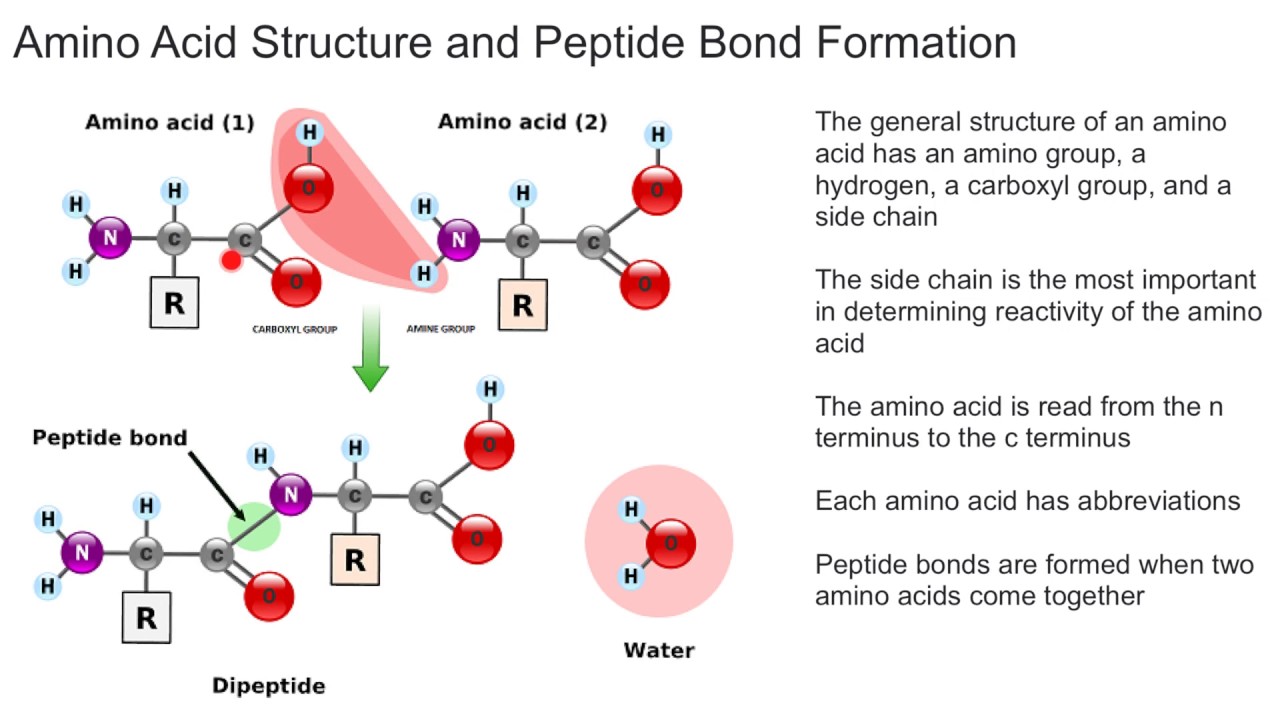
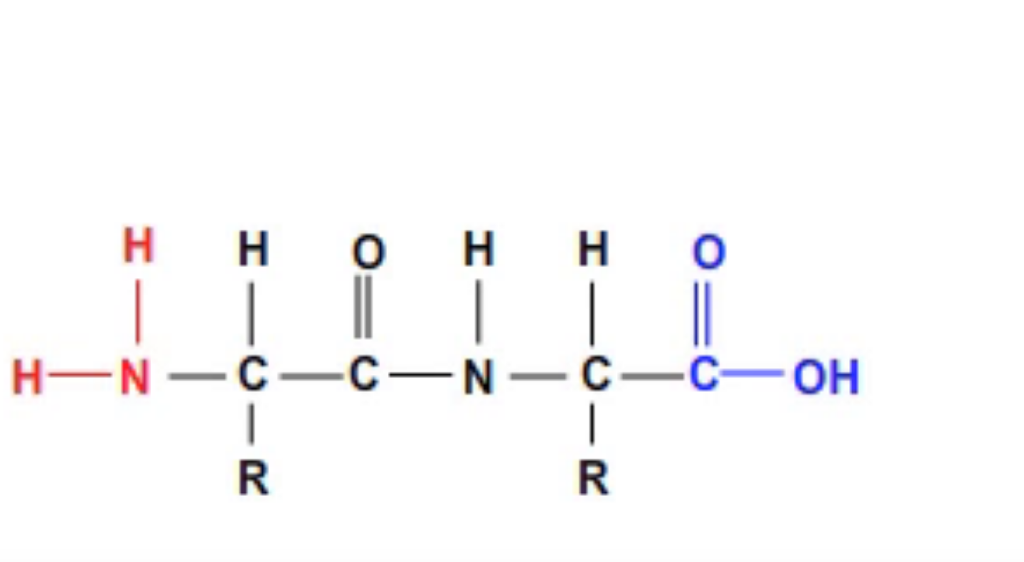
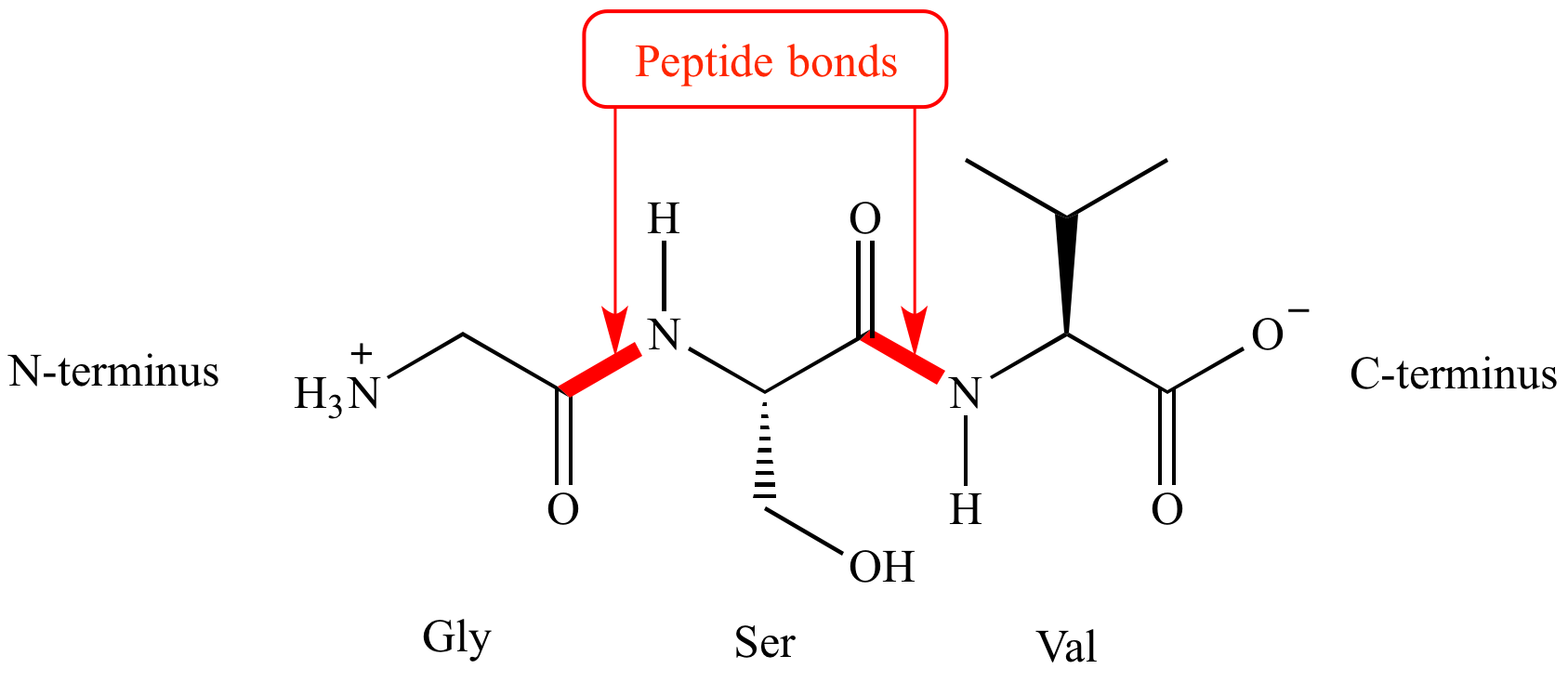
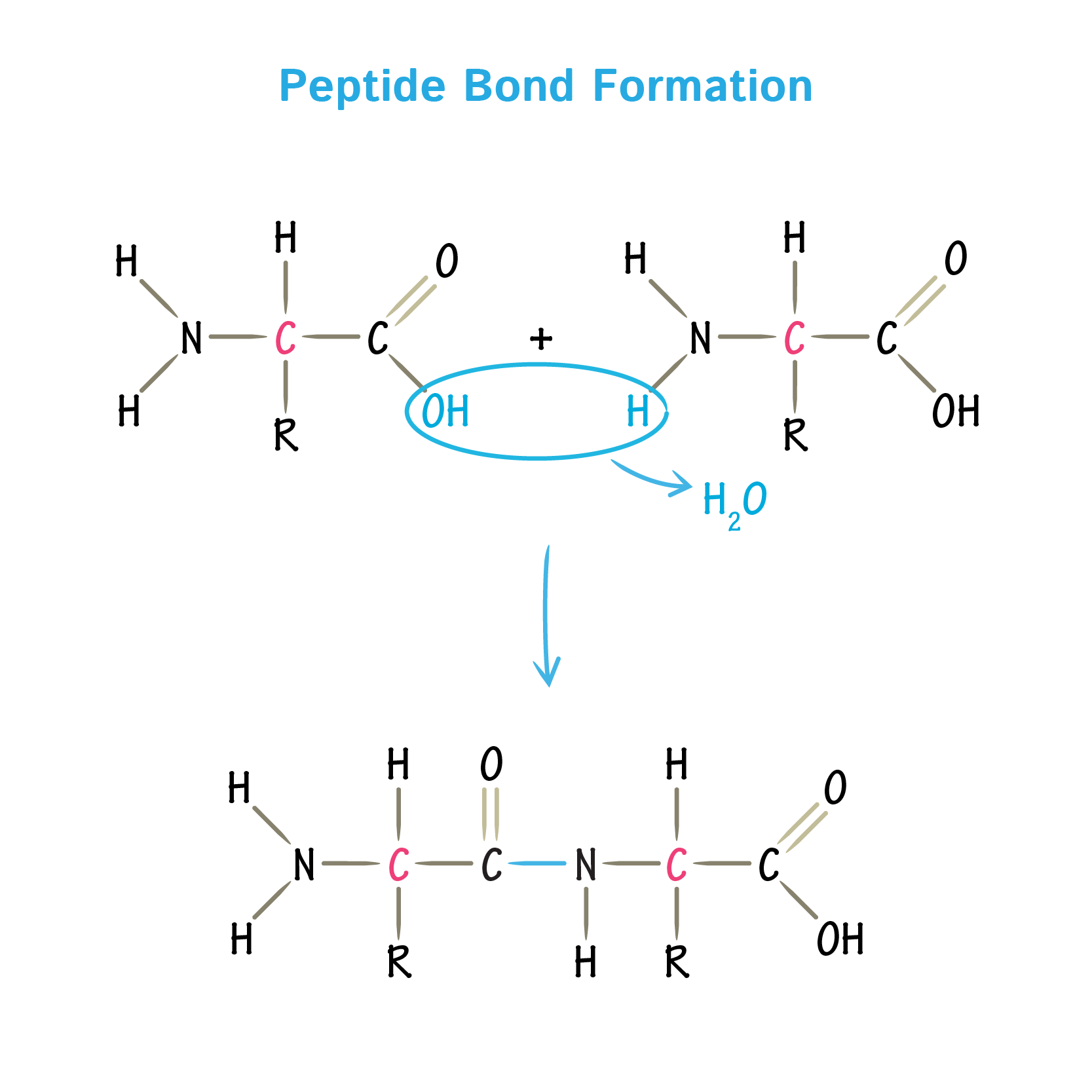
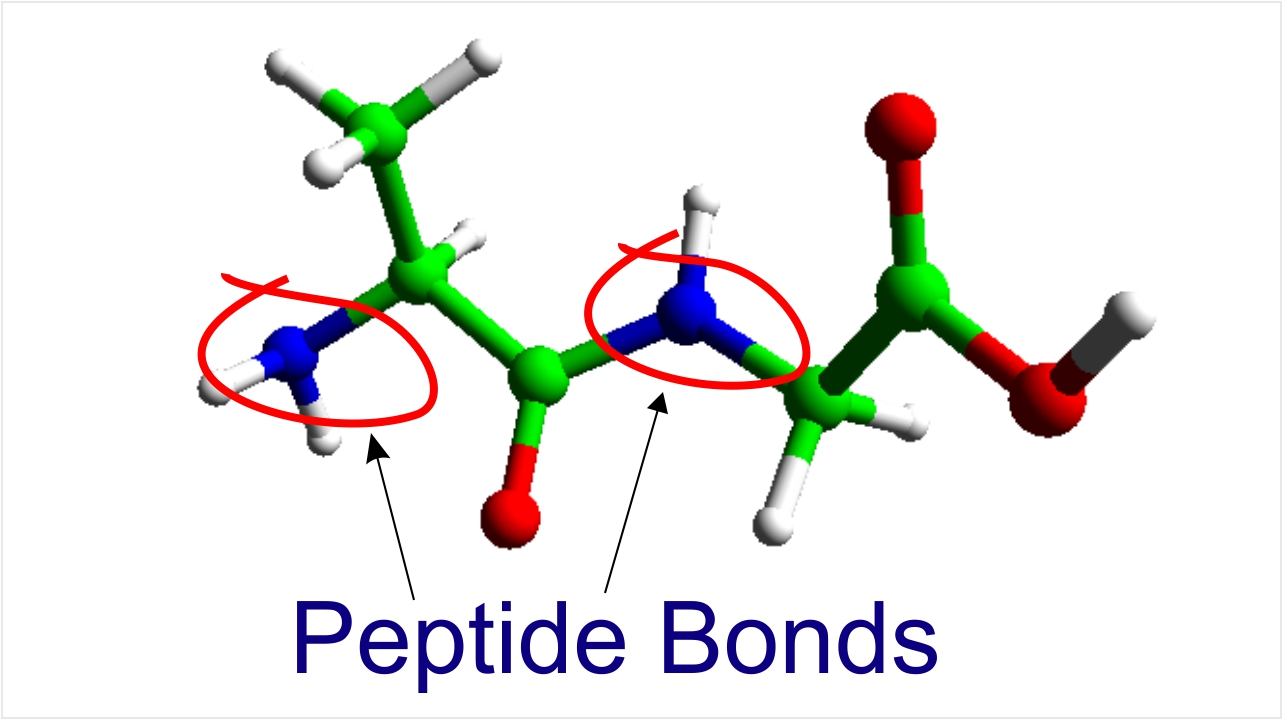
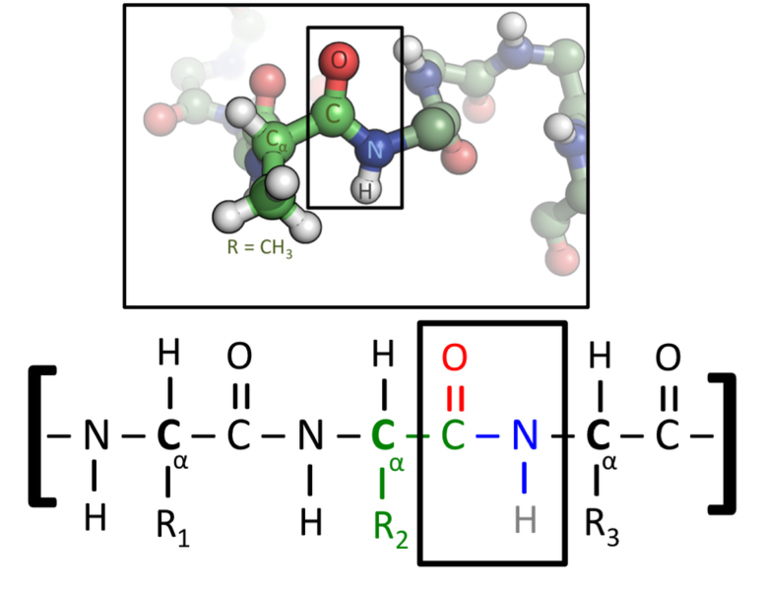
Peptide Bonds Form Between
Peptide Bonds Form Between - Web a peptide bond forms when the amino group of one amino acid bonds to the carboxyl group of another amino acid. When to amino acids come together to bond, and from the first amino acid h atom goes to form water with oh group of the second amino acid. The result is a planar structure that is stabilized by. Web a peptide bond is a chemical bond formed between two molecules when the carboxyl group of one molecule reacts with the amino group of the other molecule,. Web question • peptide bonds form between ________. Web peptides are named based on the number of amino acid residues in the sequence. Web apr 23, 2016. Polymerization is an anabolic reaction the links monomers together to. One amino acid's carboxyl group and the incoming amino acid's amino. • a) amino acids • b) an mrna codon and a trna anticodon • c) a trna and the amino acid it is carrying • d) an mrna.
When to amino acids come together to bond, and from the first amino acid h atom goes to form water with oh group of the second amino acid. Polymerization is an anabolic reaction the links monomers together to. Web apr 23, 2016. Web a covalent bond, or peptide bond, attaches to each amino acid, which a dehydration reaction forms. The result is a planar structure that is stabilized by. Web a peptide bond is a chemical bond formed between two molecules when the carboxyl group of one molecule reacts with the amino group of the other molecule,. The result is a planar structure that is stabilized by. Web peptide bond definition, a covalent bond formed by joining the carboxyl group of one amino acid to the amino group of another, with the removal of a molecule of water. Note that the product molecule still has a reactive amino group on the left and a reactive. A peptide is two or more amino acids joined together by.
The result is a planar structure that is stabilized by. Web peptide bond definition, a covalent bond formed by joining the carboxyl group of one amino acid to the amino group of another, with the removal of a molecule of water. Web peptides are named based on the number of amino acid residues in the sequence. Web a peptide bond forms when the amino group of one amino acid bonds to the carboxyl group of another amino acid. The result is a planar structure that is stabilized by. Web a peptide bond is a chemical bond formed between two molecules when the carboxyl group of one molecule reacts with the amino group of the other molecule,. Web apr 23, 2016. Web a peptide bond is formed between the amino acids during polymerization to form a protein. As peptide chains form between joining of the primary structure of amino. • a) amino acids • b) an mrna codon and a trna anticodon • c) a trna and the amino acid it is carrying • d) an mrna.
Peptide Bond Definition, Structure, Mechanism, and Examples
Web peptides are named based on the number of amino acid residues in the sequence. Web a peptide bond forms when the amino group of one amino acid bonds to the carboxyl group of another amino acid. As peptide chains form between joining of the primary structure of amino. When to amino acids come together to bond, and from the.
Amino Acid Structure and Peptide Bond Formation YouTube
Polymerization is an anabolic reaction the links monomers together to. The bond is a special linkage between the. Web apr 23, 2016. • a) amino acids • b) an mrna codon and a trna anticodon • c) a trna and the amino acid it is carrying • d) an mrna. Note that the product molecule still has a reactive amino.
Peptide bonds form when two amino acid molecules
The result is a planar structure that is stabilized by. Note that the product molecule still has a reactive amino group on the left and a reactive. Web these chains contain two or more amino acids (forming amino acid polymers) that are coupled by a peptide bond. Web peptides are named based on the number of amino acid residues in.
Illustrated Glossary of Organic Chemistry Peptide bond
Note that the product molecule still has a reactive amino group on the left and a reactive. The result is a planar structure that is stabilized by. Polymerization is an anabolic reaction the links monomers together to. Web a peptide bond forms when the amino group of one amino acid bonds to the carboxyl group of another amino acid. •.
Amino acids physical, chemical properties and peptide bond
A peptide is two or more amino acids joined together by. One amino acid's carboxyl group and the incoming amino acid's amino. Web apr 23, 2016. Web question • peptide bonds form between ________. The result is a planar structure that is stabilized by.
January 2019 Biology Exams 4 U
Web these chains contain two or more amino acids (forming amino acid polymers) that are coupled by a peptide bond. Web a covalent bond, or peptide bond, attaches to each amino acid, which a dehydration reaction forms. Web a peptide bond is formed between the amino acids during polymerization to form a protein. Note that the product molecule still has.
Why Is Eating Meat So Unhealthy Dr. Bob McCauley's Blog
The result is a planar structure that is stabilized by. Web a covalent bond, or peptide bond, attaches to each amino acid, which a dehydration reaction forms. A peptide is two or more amino acids joined together by. Web these chains contain two or more amino acids (forming amino acid polymers) that are coupled by a peptide bond. Web a.
Peptide Bond Definition, Formation, Structure, Examples
Web peptide bond definition, a covalent bond formed by joining the carboxyl group of one amino acid to the amino group of another, with the removal of a molecule of water. • a) amino acids • b) an mrna codon and a trna anticodon • c) a trna and the amino acid it is carrying • d) an mrna. Web.
Formation of peptide bonds. Peptide bond, Pearson education, Physiology
The bond is a special linkage between the. One amino acid's carboxyl group and the incoming amino acid's amino. The result is a planar structure that is stabilized by. Web a peptide bond forms when the amino group of one amino acid bonds to the carboxyl group of another amino acid. • a) amino acids • b) an mrna codon.
What Are Proteins? Amino Acids, Peptide Bonds
A peptide is two or more amino acids joined together by. Web question • peptide bonds form between ________. Web a covalent bond, or peptide bond, attaches to each amino acid, which a dehydration reaction forms. Web apr 23, 2016. Web these chains contain two or more amino acids (forming amino acid polymers) that are coupled by a peptide bond.
The Result Is A Planar Structure That Is Stabilized By.
Web apr 23, 2016. Polymerization is an anabolic reaction the links monomers together to. When to amino acids come together to bond, and from the first amino acid h atom goes to form water with oh group of the second amino acid. As peptide chains form between joining of the primary structure of amino.
• A) Amino Acids • B) An Mrna Codon And A Trna Anticodon • C) A Trna And The Amino Acid It Is Carrying • D) An Mrna.
A peptide is two or more amino acids joined together by. Note that the product molecule still has a reactive amino group on the left and a reactive. Web these chains contain two or more amino acids (forming amino acid polymers) that are coupled by a peptide bond. Web question • peptide bonds form between ________.
Web Peptides Are Named Based On The Number Of Amino Acid Residues In The Sequence.
The result is a planar structure that is stabilized by. Web a peptide bond is formed between the amino acids during polymerization to form a protein. Web a covalent bond, or peptide bond, attaches to each amino acid, which a dehydration reaction forms. Web an amide bond joining two amino acid units is called a peptide bond.
Web A Peptide Bond Forms When The Amino Group Of One Amino Acid Bonds To The Carboxyl Group Of Another Amino Acid.
The bond is a special linkage between the. One amino acid's carboxyl group and the incoming amino acid's amino. Web a peptide bond is a chemical bond formed between two molecules when the carboxyl group of one molecule reacts with the amino group of the other molecule,. Web peptide bond definition, a covalent bond formed by joining the carboxyl group of one amino acid to the amino group of another, with the removal of a molecule of water.