What Kinds Of Substances Typically Form Amorphous Solids
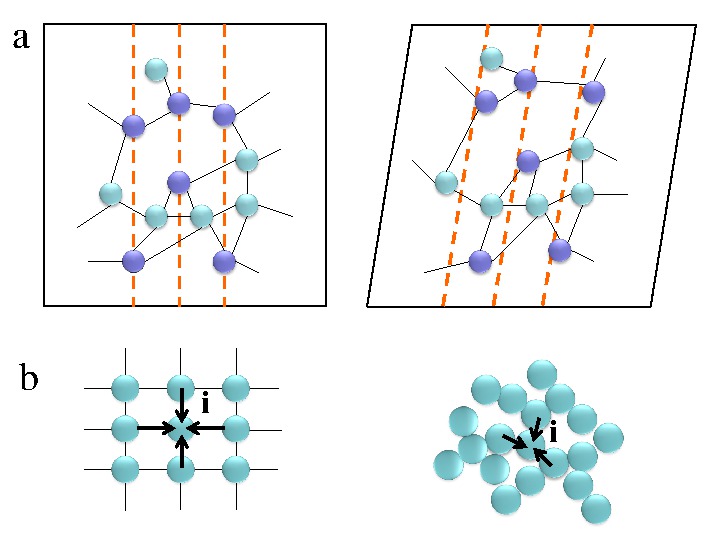
What Kinds Of Substances Typically Form Amorphous Solids - They lack any internal structure. Metals and ionic compounds typically. Substances that consist of large molecules, or a mixture of molecules whose movements are more. Crystalline solids have a definite. Web molecular what kinds of substances typically form amorphous solids? A ionic compounds o small. Web metals and ionic compounds typically form ordered, crystalline solids. Web solid is one of the three main states of matter, along with liquid and gas. The entities of a solid phase may be arranged in a regular, repeating pattern (crystalline solids) or randomly (amorphous). Web substances that consist of large molecules, or a mixture of molecules whose movements are more restricted, often form amorphous solids.
Substances that consist of large molecules, or a mixture of molecules whose movements are more. A ionic compounds o small. They lack any internal structure. Web an amorphous solid has no distinct form, either mathematical or translucent. Metals and ionic compounds typically. They are opposite to crystalline solids , which have a defined shape,. Web metals and ionic compounds typically form ordered, crystalline solids. Web solid is one of the three main states of matter, along with liquid and gas. Web an amorphous solid is a solid whose atoms are not in a regular crystalline pattern. Matter is the stuff of the universe, the atoms, molecules and ions that make up all.
The word amorphous comes from the greek word ámorphos, which means. Web 7,567 the definition of amorphous should be one that is readily understandable, accessible and provable for infringement purposes. They lack any internal structure. They are opposite to crystalline solids , which have a defined shape,. Web an amorphous solid has no distinct form, either mathematical or translucent. Web molecular what kinds of substances typically form amorphous solids? Large neutral molecules which of these substances will not form a covalent network solid? Web metals and ionic compounds typically form ordered, crystalline solids. Web metals and ionic compounds typically form ordered, crystalline solids. The substances that appear like solids but do not have well developed perfectly ordered crystalline structures are called amorphous (no form).
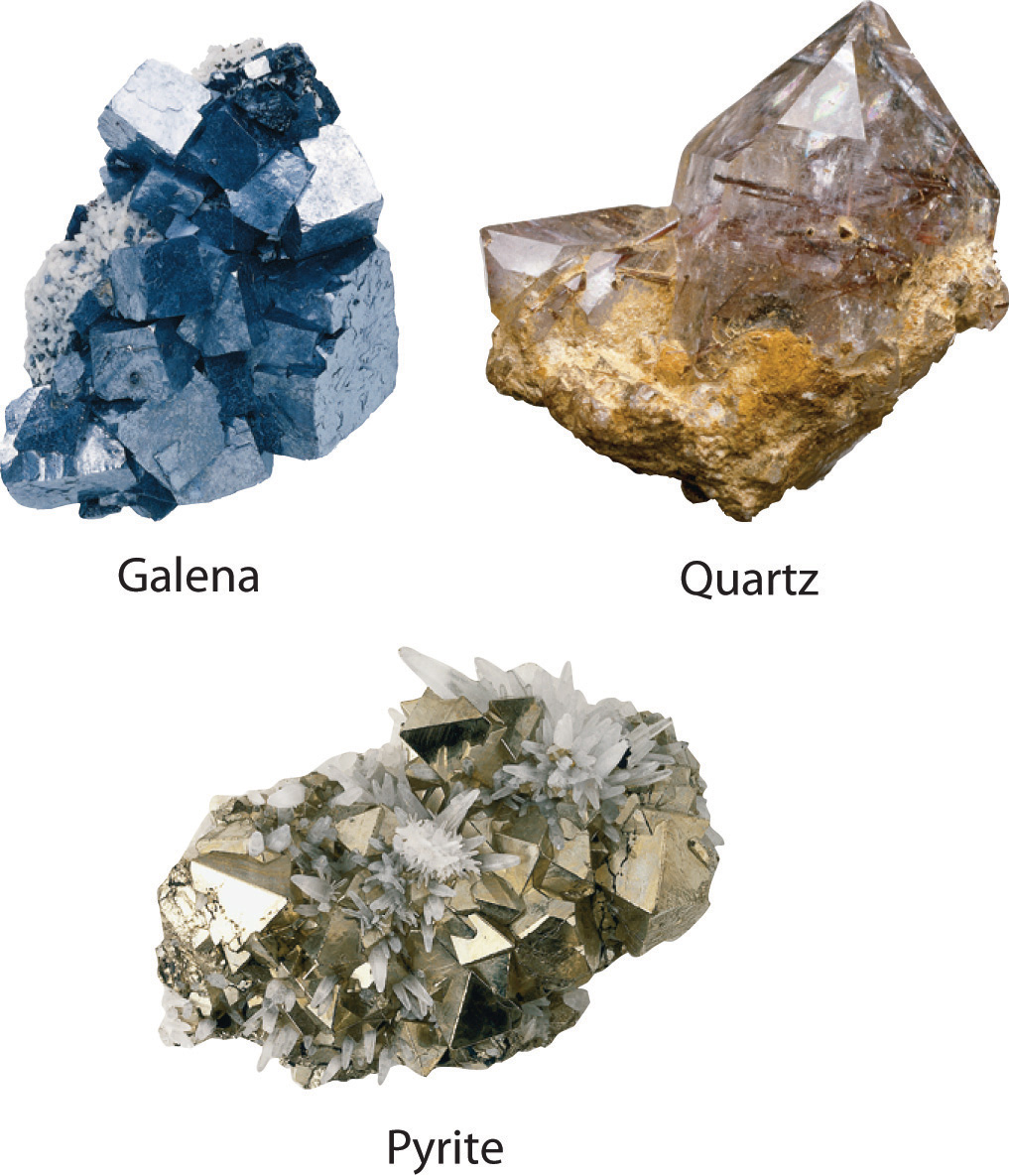
Example of Solids Crystalline solids and Amorphous solids
The word amorphous comes from the greek word ámorphos, which means. They lack any internal structure. Web an amorphous solid has no distinct form, either mathematical or translucent. Substances that consist of large molecules, or a mixture of molecules whose movements are more. Amorphous solid resemble liquids in that they do.
12.1 Crystalline and Amorphous Solids Chemistry LibreTexts
They lack any internal structure. Web chemistry chemistry questions and answers what kinds of substances typically form amorphous solids? Web molecular what kinds of substances typically form amorphous solids? A ionic compounds o small. The entities of a solid phase may be arranged in a regular, repeating pattern (crystalline solids) or randomly (amorphous).
Classical Statistical Mechanics
Web metals and ionic compounds typically form ordered, crystalline solids. A ionic compounds o small. Web an amorphous solid is a solid whose atoms are not in a regular crystalline pattern. Web solid is one of the three main states of matter, along with liquid and gas. Web 7,567 the definition of amorphous should be one that is readily understandable,.
RUDN University physicists described a new type of amorphous solid
Substances that consist of large molecules, or a mixture of molecules whose movements. Select the correct answer below: The substances that appear like solids but do not have well developed perfectly ordered crystalline structures are called amorphous (no form). Crystalline solids have a definite. Web 7,567 the definition of amorphous should be one that is readily understandable, accessible and provable.
Crystalline & Amorphous Solids Notes
The word amorphous comes from the greek word ámorphos, which means. Metals and ionic compounds typically. Substances that consist of large molecules, or a mixture of molecules whose movements are more. A ionic compounds o small. Web chemistry chemistry questions and answers what kinds of substances typically form amorphous solids?
amorphous solid Katy Perry Buzz
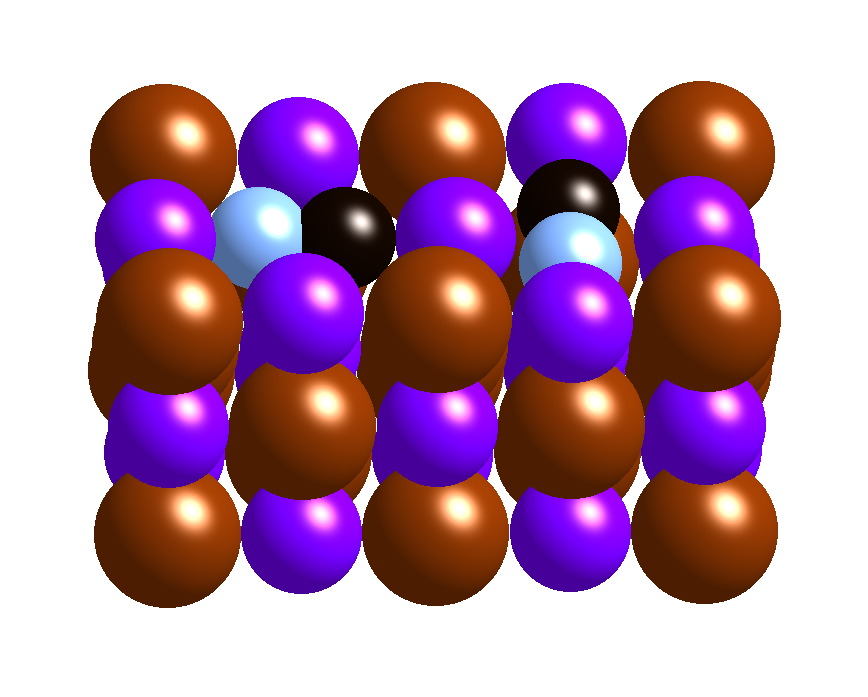
Substances that consist of large molecules, or a mixture of molecules whose movements are more. Web metals and ionic compounds typically form ordered, crystalline solids. Web 7,567 the definition of amorphous should be one that is readily understandable, accessible and provable for infringement purposes. Examples include glass and many plastics, both of which are composed of long chains of molecules.
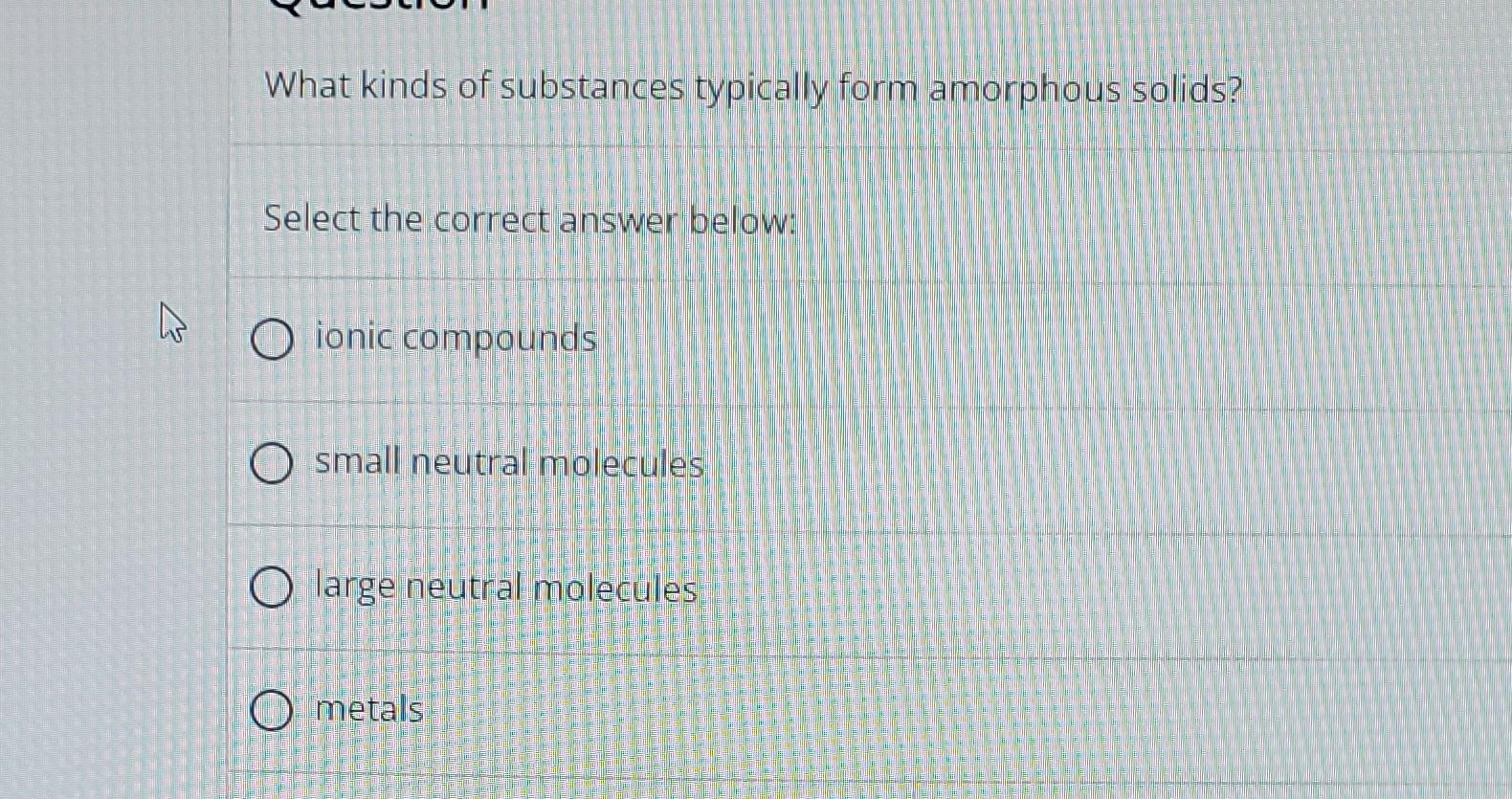
Solved What kinds of substances typically form amorphous
They are opposite to crystalline solids , which have a defined shape,. Substances that consist of large molecules, or a mixture of molecules whose movements. Examples include glass and many plastics, both of which are composed of long chains of molecules with no. Web an amorphous solid is a solid whose atoms are not in a regular crystalline pattern. A.
PPT Crystals PowerPoint Presentation ID153497
Web metals and ionic compounds typically form ordered, crystalline solids. Web 7,567 the definition of amorphous should be one that is readily understandable, accessible and provable for infringement purposes. The entities of a solid phase may be arranged in a regular, repeating pattern (crystalline solids) or randomly (amorphous). Web an amorphous solid has no distinct form, either mathematical or translucent..
Crystalline & Amorphous Solids Notes
Metals and ionic compounds typically. Substances that consist of large molecules, or a mixture of molecules whose movements are more. Substances that consist of large molecules, or a mixture of molecules whose movements. The entities of a solid phase may be arranged in a regular, repeating pattern (crystalline solids) or randomly (amorphous). Web molecular what kinds of substances typically form.
Crystalline and Amorphous Solids Explanation, Differences, Examples, etc
Web an amorphous solid is a solid whose atoms are not in a regular crystalline pattern. They are opposite to crystalline solids , which have a defined shape,. Web chemistry chemistry questions and answers what kinds of substances typically form amorphous solids? Web metals and ionic compounds typically form ordered, crystalline solids. The word amorphous comes from the greek word.
Web Metals And Ionic Compounds Typically Form Ordered, Crystalline Solids.
The substances that appear like solids but do not have well developed perfectly ordered crystalline structures are called amorphous (no form). Web solid is one of the three main states of matter, along with liquid and gas. Substances that consist of large molecules, or a mixture of molecules whose movements are more. They lack any internal structure.
A Ionic Compounds O Small.
Metals and ionic compounds typically. Web an amorphous solid is a solid whose atoms are not in a regular crystalline pattern. A solid whose molecules do not follow any pattern is said to be an amorphous solid. Web molecular what kinds of substances typically form amorphous solids?
The Word Amorphous Comes From The Greek Word Ámorphos, Which Means.
Substances that consist of large molecules, or a mixture of molecules whose movements are more. Web metals and ionic compounds typically form ordered, crystalline solids. Web chemistry chemistry questions and answers what kinds of substances typically form amorphous solids? The entities of a solid phase may be arranged in a regular, repeating pattern (crystalline solids) or randomly (amorphous).
Amorphous Solid Resemble Liquids In That They Do.
They are opposite to crystalline solids , which have a defined shape,. Web 7,567 the definition of amorphous should be one that is readily understandable, accessible and provable for infringement purposes. Web metals and ionic compounds typically form ordered, crystalline solids. Large neutral molecules which of these substances will not form a covalent network solid?