When Nucleotides Polymerize To Form A Nucleic Acid
When Nucleotides Polymerize To Form A Nucleic Acid - Each nucleotide monomer consists of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar, plus a phosphate group. However, in the absence of enzymes and metabolism. Web solution verified step 1 1 of 2 pentose sugars are combined with the phosphate group with covalent bonds on the third carbon atom (hydroxyl group; 6)when nucleotides polymerize to form a nucleic acid_ a) a covalent bond forms between the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate of a second b) covalent. Each nucleotide is made up of three components: Web the learning objective of this module is to identify the different molecules that combine to form nucleotides. A nitrogenous base (for which there are five. The 5' group of a nucleotide triphosphate is. Web when nucleotides polymerize to form a nucleic acid, _____. When nucleotides polymerize to form a nucleic acid, a.
The 5' group of a nucleotide triphosphate is. A nitrogenous base (for which there are five. Web when nucleotides polymerize to form a nucleic acid, _____. This process involves the covalent bond formation between the two. Web click on the step numbers below to see the polymerization of nucleotides. Web when nucleotides polymerize to form a nucleic acid _____ covalent bonds form between the bases of two nucleotides a hydrogen bond forms between the sugar of one. 6)when nucleotides polymerize to form a nucleic acid_ a) a covalent bond forms between the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate of a second b) covalent. Web when nucleotides polymerize to form a nucleic acid, ________. A) a covalent bond forms between the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate of a second. However, in the absence of enzymes and metabolism.
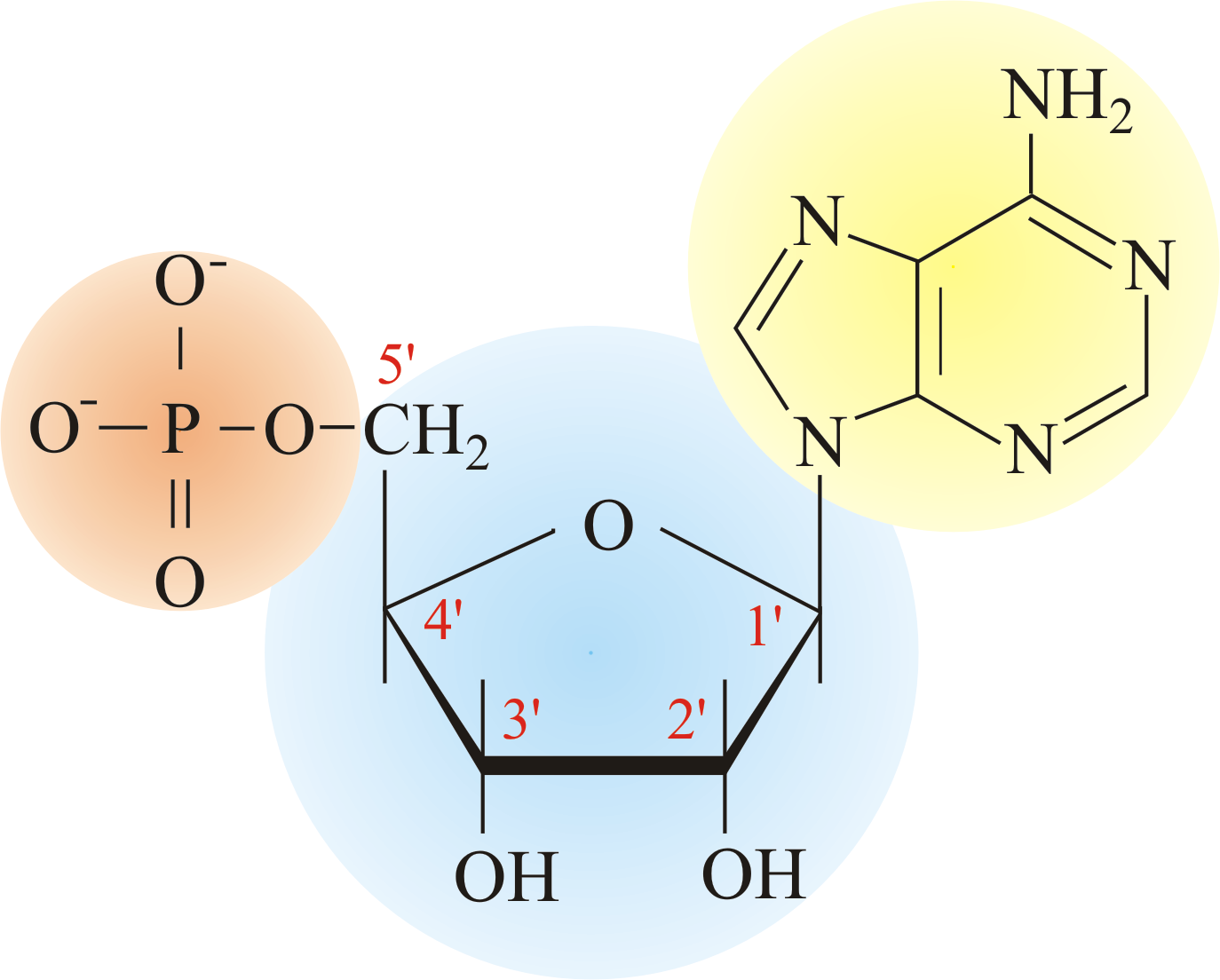
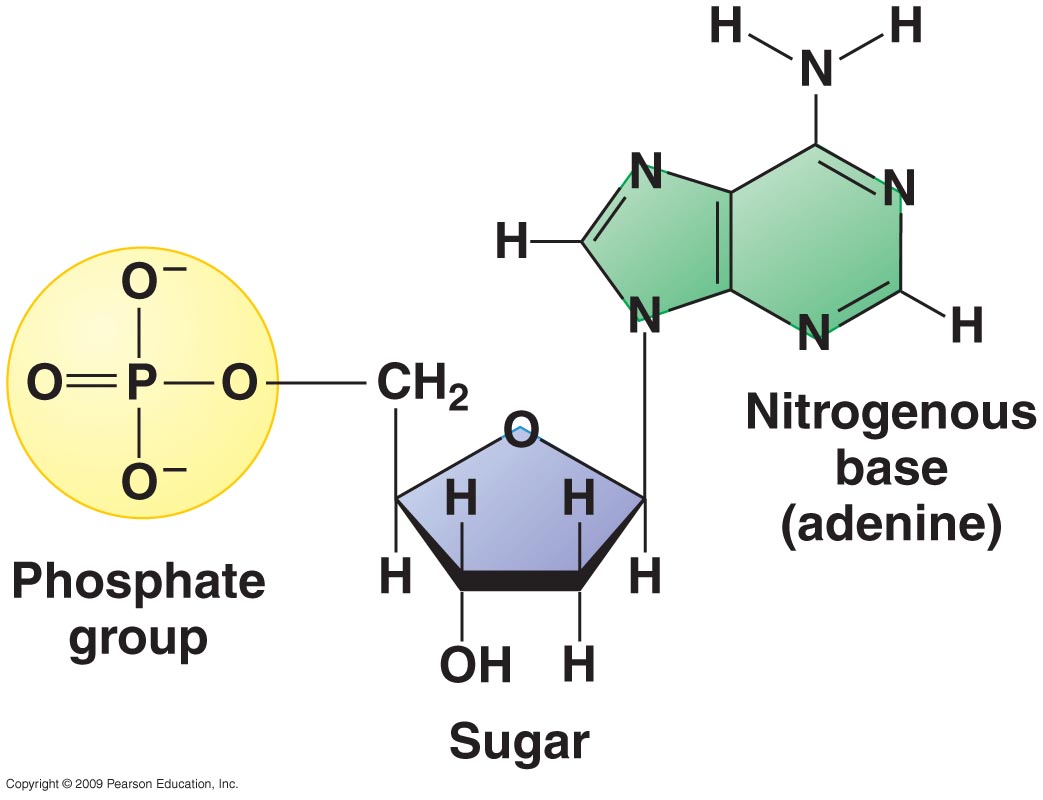
Each nucleotide monomer consists of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar, plus a phosphate group. When nucleotides polymerize to form a nucleic acid, a. True nucleotides are linked together by phos. The repeating, or monomer, units that are linked. A) a covalent bond forms between the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate of a second. Web the single unit of a whole nucleotide undergoes polymerization to form the chain of nucleic acid. A) a covalent bond forms between the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate of a second b) covalent. Web when nucleotides polymerize to form a nucleic acid, ________. 1.covalent bonds form between the bases of two neucleotides, 2.a hydrogen bond forms between sugar. The 5' group of a nucleotide triphosphate is.
(Get Answer) When Nucleotides Polymerize To Form A Nucleic Acid_ A) A
Web the single unit of a whole nucleotide undergoes polymerization to form the chain of nucleic acid. Web nucleic acids are long, unbranched polymers of nucleotides. Web when nucleotides polymerize to form a nucleic acid _____. Web solution verified step 1 1 of 2 pentose sugars are combined with the phosphate group with covalent bonds on the third carbon atom.
Nucleotide Definition, Structure (3 Parts), Examples & Function
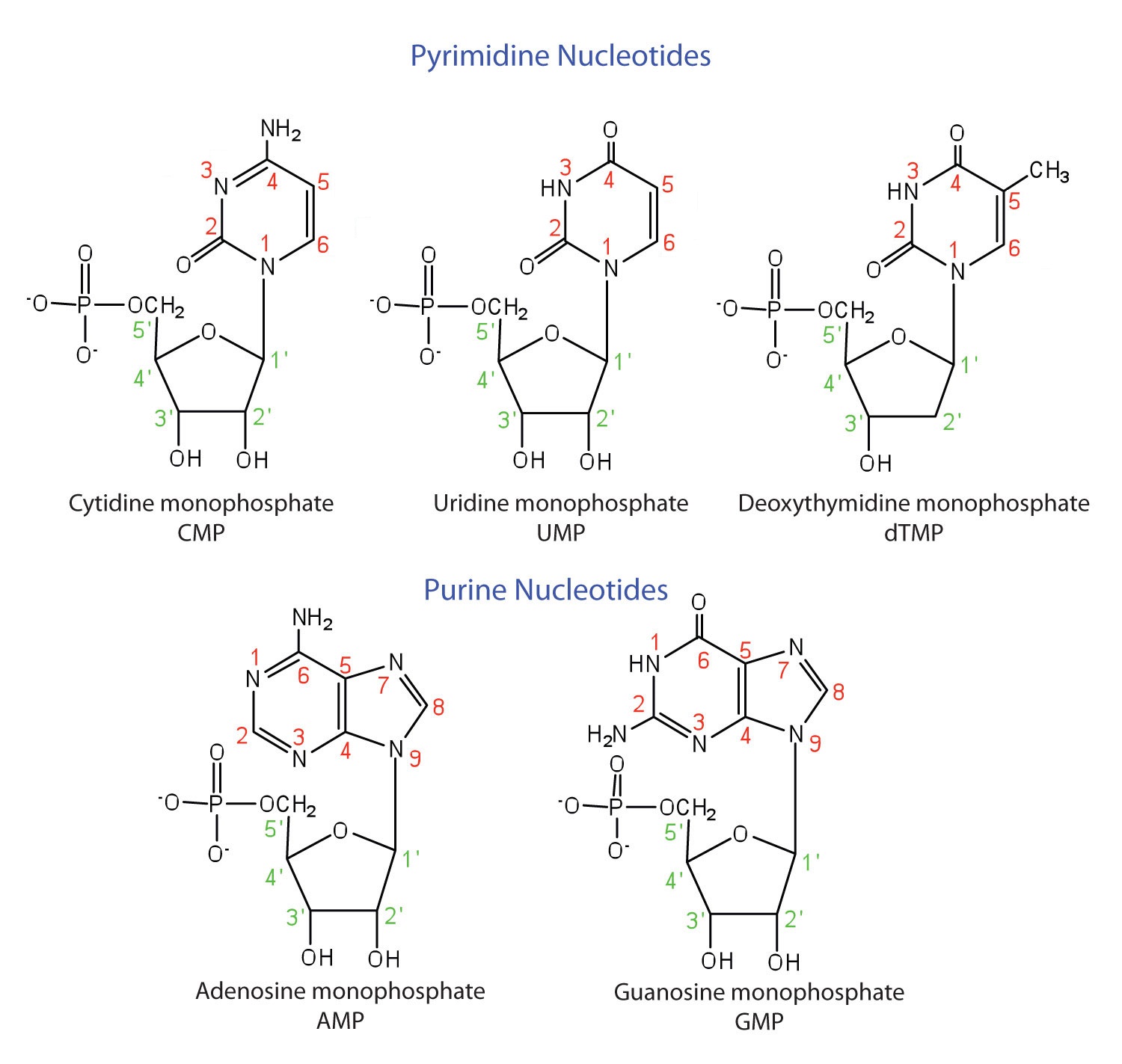
A nitrogenous base (for which there are five. The 5' group of a nucleotide triphosphate is. Web individual nucleotides condense with one another to form a nucleic acid polymer. Web the learning objective of this module is to identify the different molecules that combine to form nucleotides. Dna is a polymer of the four nucleotides a, c, g, and t,.
Nucleic Acids Definition, Examples & Functions of Nucleic acids
This process involves the covalent bond formation between the two. A) a covalent bond forms between the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate of a second. Web the learning objective of this module is to identify the different molecules that combine to form nucleotides. Web individual nucleotides condense with one another to form a nucleic acid polymer. 6)when nucleotides.
Nucleic Acids Jack's AP Biology Journal
Each nucleotide monomer consists of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar, plus a phosphate group. 1.covalent bonds form between the bases of two neucleotides, 2.a hydrogen bond forms between sugar. A) a covalent bond forms between the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate of a second b) covalent. Web when nucleotides polymerize to form a nucleic acid, ________. The.
Nucleotides and Bases Generation
1.covalent bonds form between the bases of two neucleotides, 2.a hydrogen bond forms between sugar. 6)when nucleotides polymerize to form a nucleic acid_ a) a covalent bond forms between the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate of a second b) covalent. Web nucleic acids are long, unbranched polymers of nucleotides. However, in the absence of enzymes and metabolism. Web.
3.4 Nucleic Acids The Evolution and Biology of Sex
A) a covalent bond forms between the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate of a second b) covalent. Web when nucleotides polymerize to form a nucleic acid, ________. The 5' group of a nucleotide triphosphate is. Dna is a polymer of the four nucleotides a, c, g, and t, which are joined through a backbone of alternating. Web nucleic.
When Nucleotides Polymerise To Form A Nucleic Acid
Web solution verified step 1 1 of 2 pentose sugars are combined with the phosphate group with covalent bonds on the third carbon atom (hydroxyl group; Each nucleotide monomer consists of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar, plus a phosphate group. This process involves the covalent bond formation between the two. Web individual nucleotides condense with one another to form.
Solved When nucleotides polymerize to form a nucleic acid
Web nucleic acids are long, unbranched polymers of nucleotides. Web individual nucleotides condense with one another to form a nucleic acid polymer. Web when nucleotides polymerize to form a nucleic acid _____. Each nucleotide monomer consists of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar, plus a phosphate group. When nucleotides polymerize to form a nucleic acid, a.
What is Three Parts of Nucleotide
A nitrogenous base (for which there are five. Red circle) of one pentose. Web the learning objective of this module is to identify the different molecules that combine to form nucleotides. 6)when nucleotides polymerize to form a nucleic acid_ a) a covalent bond forms between the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate of a second b) covalent. Each nucleotide.
28.1 Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids Chemistry LibreTexts
Click on the mouse at left to clear the images and text. The 5' group of a nucleotide triphosphate is. Web when nucleotides polymerize to form a nucleic acid, ________. However, in the absence of enzymes and metabolism. A) a covalent bond forms between the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate of a second.
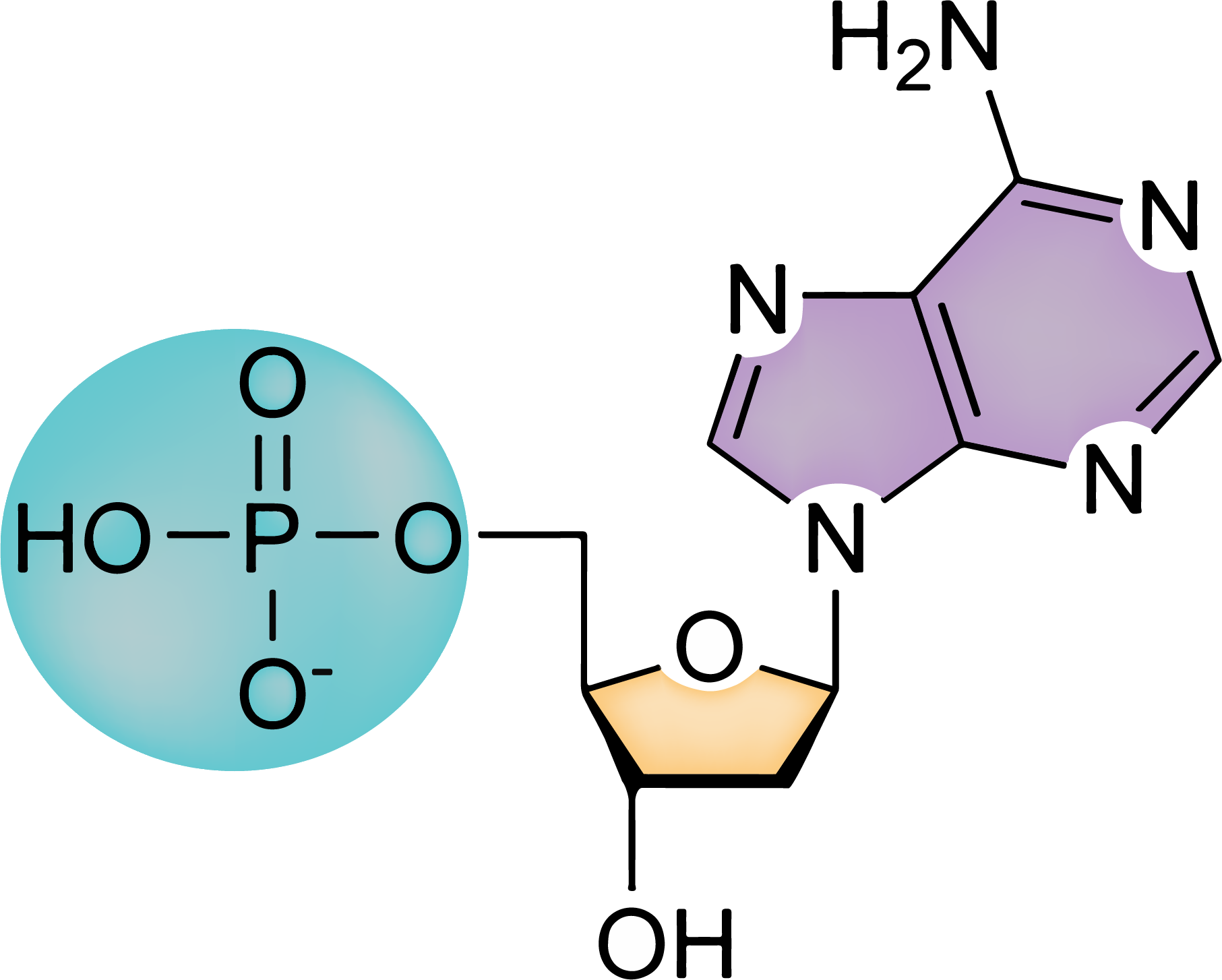
Web Polymerization Of Nucleotides Occurs In A Condensation Reaction In Which Phosphodiester Bonds Are Formed.
Click on the mouse at left to clear the images and text. Red circle) of one pentose. Dna is a polymer of the four nucleotides a, c, g, and t, which are joined through a backbone of alternating. Web the learning objective of this module is to identify the different molecules that combine to form nucleotides.
This Process Involves The Covalent Bond Formation Between The Two.
The repeating, or monomer, units that are linked. Web individual nucleotides condense with one another to form a nucleic acid polymer. Web when nucleotides polymerize to form a nucleic acid, ________. Each nucleotide is made up of three components:
Each Nucleotide Monomer Consists Of A Nitrogenous Base, A Pentose Sugar, Plus A Phosphate Group.
Web when nucleotides polymerize to form a nucleic acid _____. Web the single unit of a whole nucleotide undergoes polymerization to form the chain of nucleic acid. A) a covalent bond forms between the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate of a second. When nucleotides polymerize to form a nucleic acid, a.
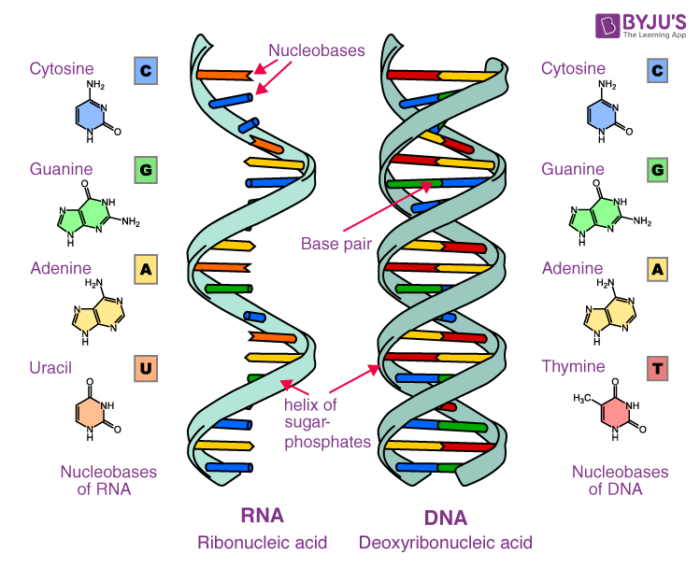
Web Nucleic Acids Are Long, Unbranched Polymers Of Nucleotides.
True nucleotides are linked together by phos. Web when nucleotides polymerize to form a nucleic acid _____ covalent bonds form between the bases of two nucleotides a hydrogen bond forms between the sugar of one. However, in the absence of enzymes and metabolism. 6)when nucleotides polymerize to form a nucleic acid_ a) a covalent bond forms between the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate of a second b) covalent.