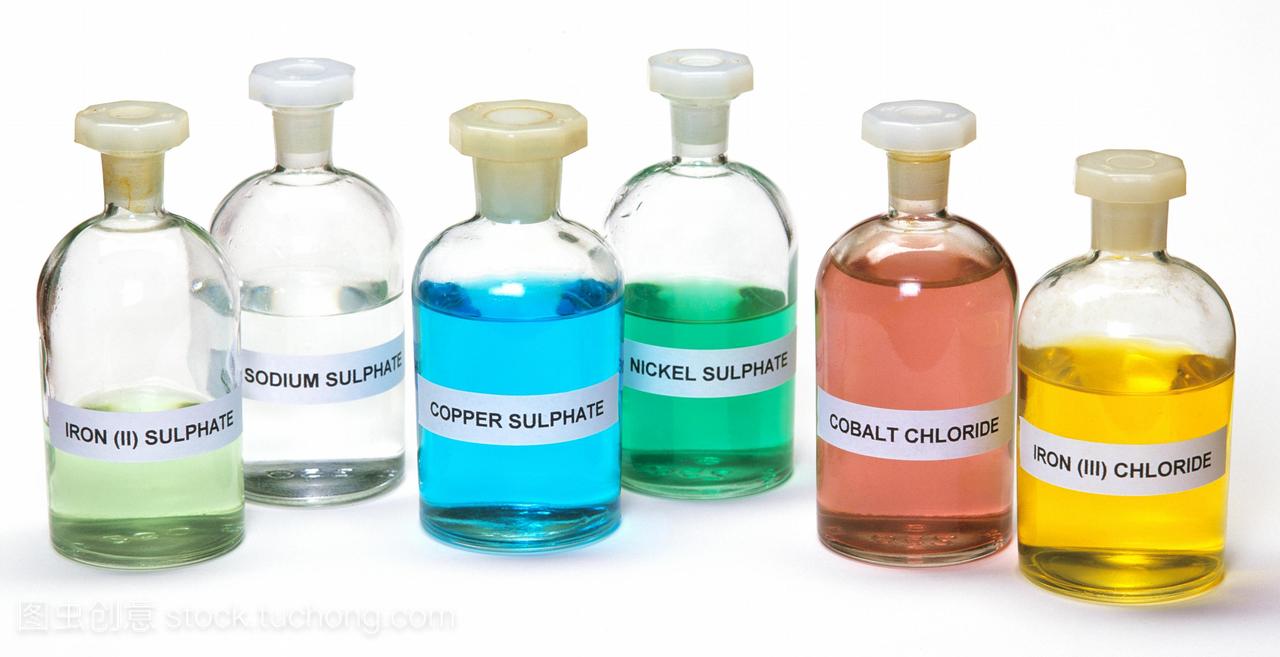
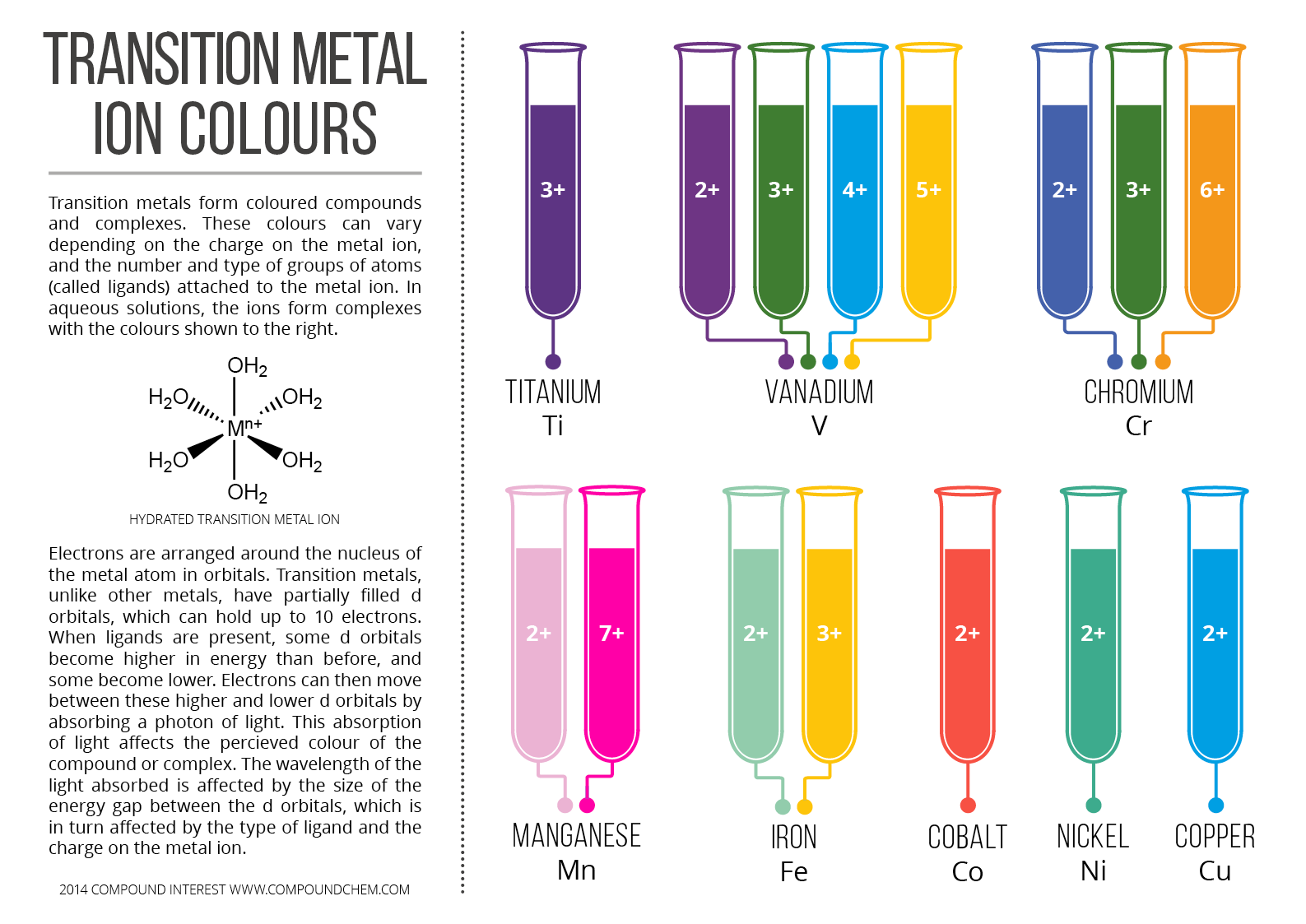
Why Transition Metals Form Coloured Compounds
Why Transition Metals Form Coloured Compounds - Web why do transition metals form coloured compounds? Web this page explains what a transition metal is in terms of its electronic structure, and then goes on to look at the general features of transition metal chemistry. Web the transition metals generally form coloured compounds. Web the transition metals are the metallic elements that serve as a bridge, or transition, between the two sides of the table. The presence of d orbitals is a common feature of transition components. Web the usual definition of a transition metal is one which forms one or more stable ions which have incompletely filled d orbitals. The d orbitals split and. Web the transition elements are metals. Web why are transition metal complexes coloured? Web the transition elements and main group elements can form coordination compounds, or complexes, in which a central metal atom or ion is bonded to one or.
Be aware that this is only an. They form coloured compounds and act as catalysts. The d orbitals split and. Transition elements form coloured compounds. They are all metals and include many. The presence of d orbitals is a common feature of transition components. Web the transition metals generally form coloured compounds. Zinc with the electronic structure [ar]. Web this page explains what a transition metal is in terms of its electronic structure, and then goes on to look at the general features of transition metal chemistry. Web the transition metals are the metallic elements that serve as a bridge, or transition, between the two sides of the table.
Web the transition metals are the metallic elements that serve as a bridge, or transition, between the two sides of the table. Web the transition elements and main group elements can form coordination compounds, or complexes, in which a central metal atom or ion is bonded to one or. Web why are transition metal complexes coloured? Bonding in simple molecules that contain transition metals this page explains what a. Transition elements form coloured compounds. Be aware that this is only an. Web feb 2, 2016 8: They have high melting points and densities, and are strong and hard. Web 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 transition metals the transition metals are in the block in the middle of the periodic table, between groups 2 and 3. Web the transition elements are metals.
Transition Metal Ion Colors
They have high melting points and densities, and are strong and hard. Web why do transition metals form coloured compounds? Web the usual definition of a transition metal is one which forms one or more stable ions which have incompletely filled d orbitals. Bonding in simple molecules that contain transition metals this page explains what a. Transition elements have 3d.
savvychemist GCSE OCR Gateway C41c Transition metal properties
They form coloured compounds and act as catalysts. Web cbse cbse study material live join vedantu’s free mastercalss explain why: Bonding in transition metal compounds and coordination complexes 8.2: Web the transition elements are metals. Web the transition elements and main group elements can form coordination compounds, or complexes, in which a central metal atom or ion is bonded to.
PPT KS4 Chemistry PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6307470
Transition elements have 3d orbitals with the same energy level however when molecules/ligands form dative covalent. Web the transition metals generally form coloured compounds. They are all metals and include many. Transition elements form coloured compounds. Zinc with the electronic structure [ar].
Transition Metals as Colored Compounds
The presence of d orbitals is a common feature of transition components. They form coloured compounds and act as catalysts. Be aware that this is only an. In their higher oxidation states, they form covalent compounds or. Web feb 2, 2016 8:
13 Transition Metals & Colored Complexes The!Mad!Scientist!
The d orbitals split and. The presence of d orbitals is a common feature of transition components. Web the transition metals are the metallic elements that serve as a bridge, or transition, between the two sides of the table. Zinc with the electronic structure [ar]. Web 3 rows transition metals have high melting points and densities, form coloured compounds and.
dblock elements 2 Explaining the origin of colour in their salts
Transition elements form coloured compounds. Zinc with the electronic structure [ar]. They form coloured compounds and act as catalysts. They have high melting points and densities, and are strong and hard. Web this page explains what a transition metal is in terms of its electronic structure, and then goes on to look at the general features of transition metal chemistry.
science chemistry compound transition metals Fundamental Photographs
Transition metals and their many compounds act as good catalyst. Answer verified 237.9k + views. Transition elements have 3d orbitals with the same energy level however when molecules/ligands form dative covalent. Web the transition elements are metals. They form coloured compounds and act as catalysts.
SPMStraightA — Transition Metals make coloured compounds
Be aware that this is only an. Zinc with the electronic structure [ar]. Web why are transition metal complexes coloured? They form coloured compounds and act as catalysts. Transition elements have 3d orbitals with the same energy level however when molecules/ligands form dative covalent.
PPT Transition Metal Chemistry PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Web 3 rows transition metals have high melting points and densities, form coloured compounds and act as. Transition elements have 3d orbitals with the same energy level however when molecules/ligands form dative covalent. The presence of d orbitals is a common feature of transition components. Web this page explains what a transition metal is in terms of its electronic structure,.
硫酸铜溶液是什么颜色_硫酸铜溶液的颜色_微信公众号文章
Bonding in simple molecules that contain transition metals this page explains what a. Web the transition elements are metals. Transition elements form coloured compounds. The presence of d orbitals is a common feature of transition components. They are all metals and include many.
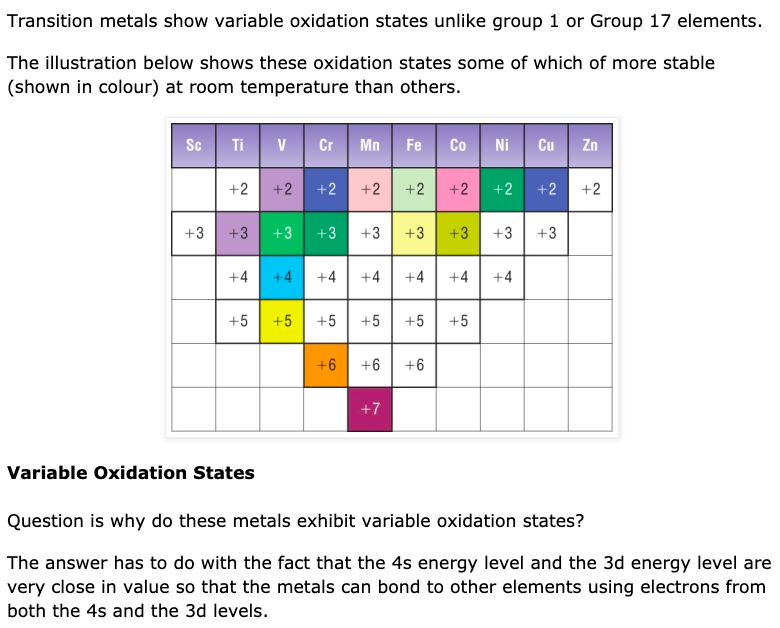
Web In Their Lower Oxidation States, The Transition Elements Form Ionic Compounds;
Web the transition metals generally form coloured compounds. Web the transition elements and main group elements can form coordination compounds, or complexes, in which a central metal atom or ion is bonded to one or. They have high melting points and densities, and are strong and hard. Web feb 2, 2016 8:
Web Cbse Cbse Study Material Live Join Vedantu’s Free Mastercalss Explain Why:
They form coloured compounds and act as catalysts. Web why do transition metals form coloured compounds? Zinc with the electronic structure [ar]. Web 3 rows transition metals have high melting points and densities, form coloured compounds and act as.
Bonding In Transition Metal Compounds And Coordination Complexes 8.2:
Be aware that this is only an. The lanthanides and the actinides at the bottom of. They are all metals and include many. Web 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 transition metals the transition metals are in the block in the middle of the periodic table, between groups 2 and 3.
Web Why Are Transition Metal Complexes Coloured?
Web the transition elements are metals. The d orbitals split and. In their higher oxidation states, they form covalent compounds or. Transition metals and their many compounds act as good catalyst.