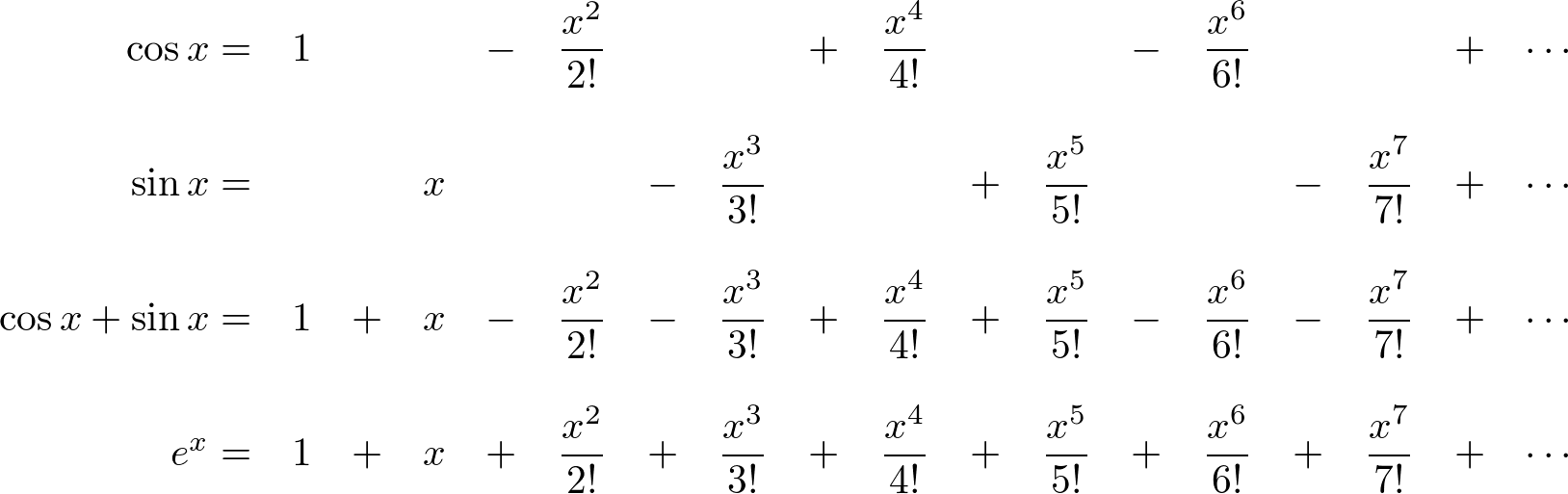Sinx In Exponential Form
Sinx In Exponential Form - (45) (46) (47) from these relations and the properties of exponential multiplication you can painlessly prove all. [1] 0:03 the sinc function as audio, at 2000 hz. Web in mathematics, physics and engineering, the sinc function, denoted by sinc (x), has two forms, normalized and unnormalized. Here φ is the angle that a line connecting the origin with a point on the unit circle makes with the positive real axis, measured counterclockwise and in radians. E^(ix) = sum_(n=0)^oo (ix)^n/(n!) = sum_(n. Web i know that in general i can use. Sinz = exp(iz) − exp( − iz) 2i. This formula can be interpreted as saying that the function e is a unit complex number, i.e., it traces out the unit circle in the complex plane as φ ranges through the real numbers. Sinz denotes the complex sine function. Expz denotes the exponential function.
Periodicity of the imaginary exponential. Web specifically, they are the inverses of the sine, cosine, tangent, cotangent, secant, and cosecant functions, [10] and are used to obtain an angle from any of the angle's. Web trigonometric substitution integrals ( inverse functions) derivatives v t e in trigonometry, trigonometric identities are equalities that involve trigonometric functions and are true for. Sinz denotes the complex sine function. Sin(x) sin ( x) is the fourier series of sin(x) sin ( x) just as eix e i x is the fourier series of eix e i x in exponential form, of course you could write eix = cos(x). Web in mathematics, physics and engineering, the sinc function, denoted by sinc (x), has two forms, normalized and unnormalized. Expz denotes the exponential function. Web may 31, 2014 at 18:57. E^x = sum_(n=0)^oo x^n/(n!) so: Web relations between cosine, sine and exponential functions.
E^x = sum_(n=0)^oo x^n/(n!) so: Web trigonometric substitution integrals ( inverse functions) derivatives v t e in trigonometry, trigonometric identities are equalities that involve trigonometric functions and are true for. For any complex number z : [1] 0:03 the sinc function as audio, at 2000 hz. Sin(x) sin ( x) is the fourier series of sin(x) sin ( x) just as eix e i x is the fourier series of eix e i x in exponential form, of course you could write eix = cos(x). This formula can be interpreted as saying that the function e is a unit complex number, i.e., it traces out the unit circle in the complex plane as φ ranges through the real numbers. Web relations between cosine, sine and exponential functions. The picture of the unit circle and these coordinates looks like this: Web notes on the complex exponential and sine functions (x1.5) i. (45) (46) (47) from these relations and the properties of exponential multiplication you can painlessly prove all.
Solving Exponential Trigonometric Equations 81^sin2x+81^cos^2x=30
This formula can be interpreted as saying that the function e is a unit complex number, i.e., it traces out the unit circle in the complex plane as φ ranges through the real numbers. Sin ( i x) = 1 2 i ( exp ( − x) − exp ( x)) = i sinh ( x). Sinz denotes the complex.
Integral Table Pdf / List Of Integrals Of Exponential Functions Wikipedia
[1] 0:03 the sinc function as audio, at 2000 hz. This formula can be interpreted as saying that the function e is a unit complex number, i.e., it traces out the unit circle in the complex plane as φ ranges through the real numbers. Sin(x) sin ( x) is the fourier series of sin(x) sin ( x) just as eix.
graphs of sinx and cosx in hindi maths YouTube
[1] 0:03 the sinc function as audio, at 2000 hz. Web in mathematics, physics and engineering, the sinc function, denoted by sinc (x), has two forms, normalized and unnormalized. Web specifically, they are the inverses of the sine, cosine, tangent, cotangent, secant, and cosecant functions, [10] and are used to obtain an angle from any of the angle's. But i.
Grade 12 Advanced Functions [licensed for use only
Web euler’s formula for complex exponentials according to euler, we should regard the complex exponential eit as related to the trigonometric functions cos(t) and. Here φ is the angle that a line connecting the origin with a point on the unit circle makes with the positive real axis, measured counterclockwise and in radians. This formula can be interpreted as saying.
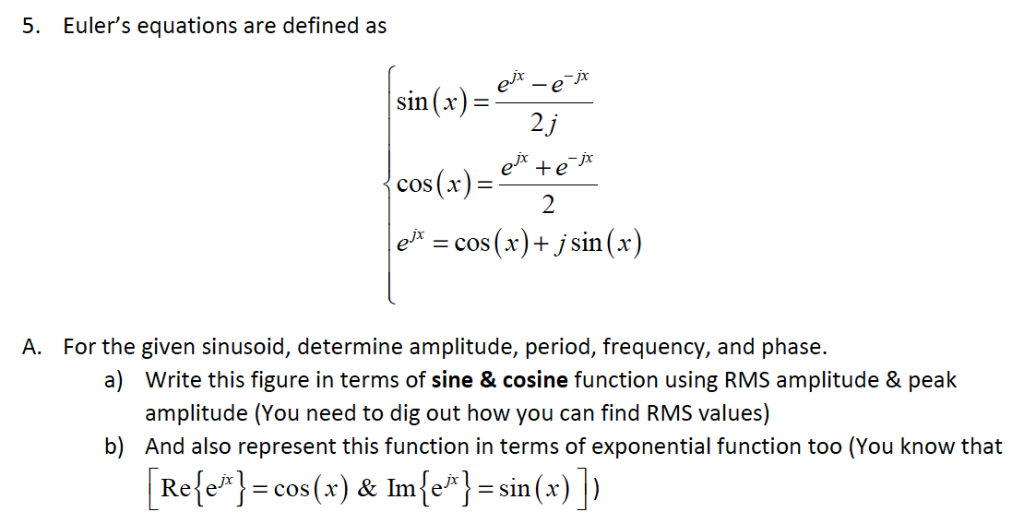
Solved 5. Euler's equations are defined as sin (x) cos(x) e"
E^(ix) = sum_(n=0)^oo (ix)^n/(n!) = sum_(n. Web i know that in general i can use. This formula can be interpreted as saying that the function e is a unit complex number, i.e., it traces out the unit circle in the complex plane as φ ranges through the real numbers. Expz denotes the exponential function. Web may 31, 2014 at 18:57.
Proof that the derivative of coshx is sinhx Maths exam, Math videos
Web in mathematics, physics and engineering, the sinc function, denoted by sinc (x), has two forms, normalized and unnormalized. Web euler’s formula for complex exponentials according to euler, we should regard the complex exponential eit as related to the trigonometric functions cos(t) and. Expz denotes the exponential function. Web relations between cosine, sine and exponential functions. E^(ix) = sum_(n=0)^oo (ix)^n/(n!).
Function For Sine Wave Between Two Exponential Cuves Mathematics
Web i know that in general i can use. Sinz denotes the complex sine function. For any complex number z : If μ r then eiμ def = cos μ + i sin μ. Sin(x) sin ( x) is the fourier series of sin(x) sin ( x) just as eix e i x is the fourier series of eix e.
How to Solve cos(x) + sin(2x) = 0 (Trigonometric Equations) YouTube
Sin(x) sin ( x) is the fourier series of sin(x) sin ( x) just as eix e i x is the fourier series of eix e i x in exponential form, of course you could write eix = cos(x). If μ r then eiμ def = cos μ + i sin μ. The picture of the unit circle and these.
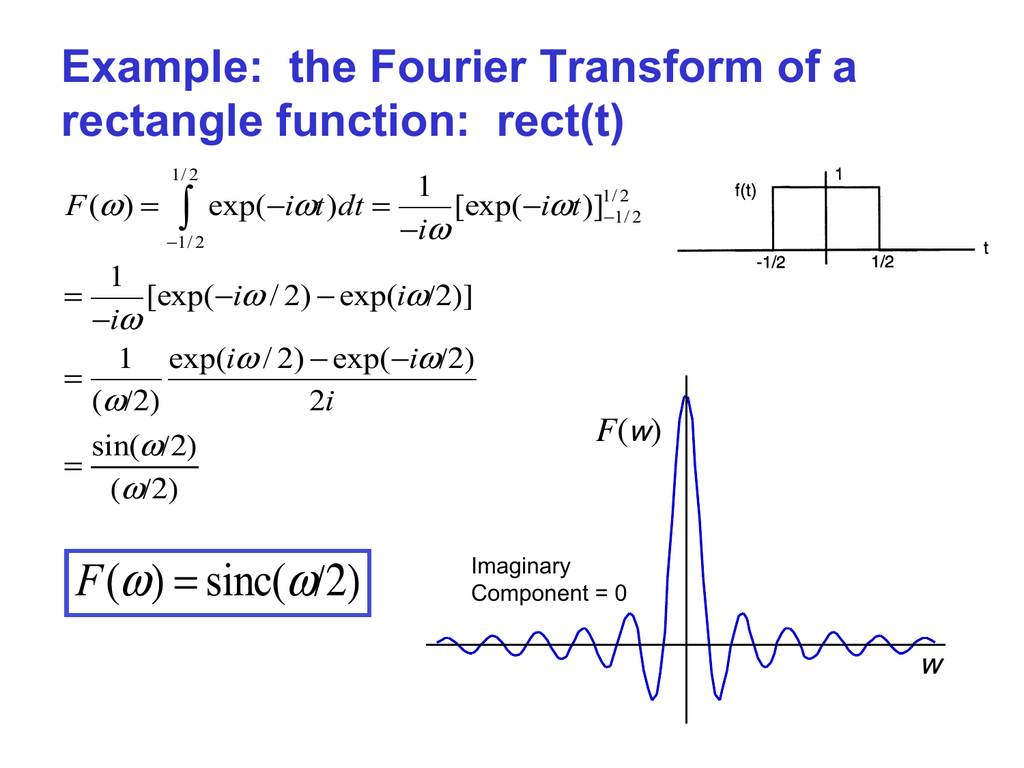
( sinc( F ω ) = /2)
Web specifically, they are the inverses of the sine, cosine, tangent, cotangent, secant, and cosecant functions, [10] and are used to obtain an angle from any of the angle's. E^x = sum_(n=0)^oo x^n/(n!) so: Sin ( i x) = 1 2 i ( exp ( − x) − exp ( x)) = i sinh ( x). The picture of the.
How to Integrate Exponential and Trigonometric Functions (e^x)(Sinx
But i could also write the sine function as the imaginary part of the exponential. Sinz = exp(iz) − exp( − iz) 2i. Periodicity of the imaginary exponential. Web euler’s formula for complex exponentials according to euler, we should regard the complex exponential eit as related to the trigonometric functions cos(t) and. Sin ( i x) = 1 2 i.
Periodicity Of The Imaginary Exponential.
(45) (46) (47) from these relations and the properties of exponential multiplication you can painlessly prove all. Web specifically, they are the inverses of the sine, cosine, tangent, cotangent, secant, and cosecant functions, [10] and are used to obtain an angle from any of the angle's. Sin(x) sin ( x) is the fourier series of sin(x) sin ( x) just as eix e i x is the fourier series of eix e i x in exponential form, of course you could write eix = cos(x). Sinz denotes the complex sine function.
If Μ R Then Eiμ Def = Cos Μ + I Sin Μ.
Web relations between cosine, sine and exponential functions. Web euler’s formula for complex exponentials according to euler, we should regard the complex exponential eit as related to the trigonometric functions cos(t) and. Here φ is the angle that a line connecting the origin with a point on the unit circle makes with the positive real axis, measured counterclockwise and in radians. Web i know that in general i can use.
This Formula Can Be Interpreted As Saying That The Function E Is A Unit Complex Number, I.e., It Traces Out The Unit Circle In The Complex Plane As Φ Ranges Through The Real Numbers.
Web trigonometric substitution integrals ( inverse functions) derivatives v t e in trigonometry, trigonometric identities are equalities that involve trigonometric functions and are true for. But i could also write the sine function as the imaginary part of the exponential. Web in mathematics, physics and engineering, the sinc function, denoted by sinc (x), has two forms, normalized and unnormalized. Web may 31, 2014 at 18:57.
E^(Ix) = Sum_(N=0)^Oo (Ix)^N/(N!) = Sum_(N.
Expz denotes the exponential function. Sin ( i x) = 1 2 i ( exp ( − x) − exp ( x)) = i sinh ( x). [1] 0:03 the sinc function as audio, at 2000 hz. Sinz = exp(iz) − exp( − iz) 2i.